Identification of Post-translationally Modified MHC Class I-Associated Peptides as Potential Cancer Immunotherapeutic Targets
- PMID: 40239839
- PMCID: PMC12362676
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mcpro.2025.100971
Identification of Post-translationally Modified MHC Class I-Associated Peptides as Potential Cancer Immunotherapeutic Targets
Abstract
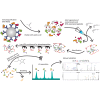
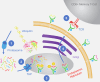
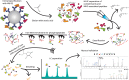
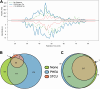
Over the past 3 decades, the Hunt laboratory has developed advancements in mass spectrometry-based technologies to enable the identification of peptides bound to major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules. The MHC class I processing pathway is responsible for presenting these peptides to circulating cytotoxic T cells, allowing them to recognize and eliminate malignant cells, many of which have aberrant signaling. Professor Hunt hypothesized that due to the dysregulation in phosphorylation in cancer that abnormal phosphopeptides could be presented by this pathway, and went on to demonstrate that this was, in fact, the case. Thereafter, the laboratory continued to sequence MHC-associated phosphopeptides and contributed several improved methods for their enrichment, detection, and sequencing. This article summarizes the most recent advancements in identification of modified MHC-associated peptides and includes the cumulative list of phosphopeptides sequenced by the Hunt lab. Further, many other post-translational modifications (PTMs) were found to modify MHC peptides, including O-GlcNAcylation, methylation, and kynurenine; in total, we present here a list of 2450 MHC-associated PTM peptides. Many of these were disease-specific and found across several patients, thus highlighting their potential as cancer immunotherapy targets. We are sharing this list with the field in hopes that it might be used in investigating this potential. Overall, the Hunt lab's contributions have significantly advanced our understanding of antigen presentation and dysregulation of PTMs, supporting modern immunotherapy and vaccine development efforts.
Keywords: MHC-associated peptides; cancer immunotherapy; immunopeptidomics; phosphorylation; post-translational modification.
Copyright © 2025 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
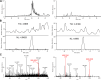
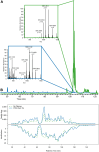
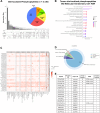
References
-
- Murphy K., Travers P., Walport M. Garland Science; New York, NY: 2008. Janeway’s Immunobiology.
-
- Klein J., Sato A. The HLA system. N. Engl. J. Med. 2000;343:702–709. - PubMed
-
- Neefjes J., Jongsma M.L.M., Paul P., Bakke O. Towards a systems understanding of MHC class I and MHC class II antigen presentation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2011;11:823–836. - PubMed
-
- Marsh S.G.E., Parham P., Barber L.D. Academic Press; San Diego, CA: 2000. The HLA FactsBook.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

