Perturbing LSD1 and WNT rewires transcription to synergistically induce AML differentiation
- PMID: 40240608
- PMCID: PMC12158781
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-025-08915-1
Perturbing LSD1 and WNT rewires transcription to synergistically induce AML differentiation
Abstract
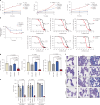
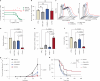
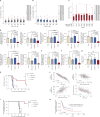
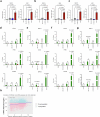
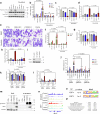
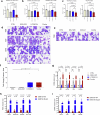
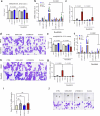
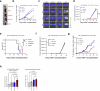
Impaired differentiation is a hallmark of myeloid malignancies1,2. Therapies that enable cells to circumvent the differentiation block, such as all-trans retinoic acid (ATRA) and arsenic trioxide (ATO), are by and large curative in acute promyelocytic leukaemia3, but whether 'differentiation therapy' is a generalizable therapeutic approach for acute myeloid leukaemia (AML) and beyond remains incompletely understood. Here we demonstrate that simultaneous inhibition of the histone demethylase LSD1 (LSD1i) and the WNT pathway antagonist GSK3 kinase4 (GSK3i) robustly promotes therapeutic differentiation of established AML cell lines and primary human AML cells, as well as reducing tumour burden and significantly extending survival in a patient-derived xenograft mouse model. Mechanistically, this combination promotes differentiation by activating genes in the type I interferon pathway via inducing expression of transcription factors such as IRF7 (LSD1i) and the co-activator β-catenin (GSK3i), and their selective co-occupancy at targets such as STAT1, which is necessary for combination-induced differentiation. Combination treatment also suppresses the canonical, pro-oncogenic WNT pathway and cell cycle genes. Analysis of datasets from patients with AML suggests a correlation between the combination-induced transcription signature and better prognosis, highlighting clinical potential of this strategy. Collectively, this combination strategy rewires transcriptional programs to suppress stemness and to promote differentiation, which may have important therapeutic implications for AML and WNT-driven cancers beyond AML.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: Y. Shi is a co-founder of K36 Therapeutics, Alternative Bio (ABio); a member of the Scientific Advisory Boards of K36 Therapeutics, ABio, Epigenica AB and Epic Bio; a board member of ABio and Epigenica AB; holds equity in Active Motif, K36 Therapeutics, Epic Bio, ABio and Epigenica AB; and serves on the Scientific Advisory Boards of School of Life Sciences, Westlake University and Westlake Laboratory of Life Sciences and Biomedicine, and Norway Centre for Embryology and Healthy Development. C.A.H. has received funding from Kronos Bio, Novartis, Oncopeptides, WNTResearch and Zentalis Pharmaceuticals for research unrelated to this study; and speaker and advisory fees from Amgen and Autolus. B.P. is a cofounder and equity holder in Alethiomics, a spin-out company from the University of Oxford; has received research funding from Alethiomics, Incyte and Galecto; and honoraria for consulting and/or paid speaking engagements from Incyte, Constellation Therapeutics, Blueprint Medicines, Novartis, GSK and BMS. All other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures






References
-
- DiNardo, C. D., Erba, H. P., Freeman, S. D. & Wei, A. H. Acute myeloid leukaemia. Lancet401, 2073–2086 (2023). - PubMed
-
- Döhner, H. et al. Diagnosis and management of AML in adults: 2022 recommendations from an international expert panel on behalf of the ELN. Blood140, 1345–1377 (2022). - PubMed
-
- De Thé, H. Differentiation therapy revisited. Nat. Rev. Cancer18, 117–127 (2018). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

