Elevated mitochondrial membrane potential is a therapeutic vulnerability in Dnmt3a-mutant clonal hematopoiesis
- PMID: 40240771
- PMCID: PMC12003737
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-57238-2
Elevated mitochondrial membrane potential is a therapeutic vulnerability in Dnmt3a-mutant clonal hematopoiesis
Abstract
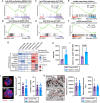
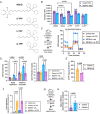
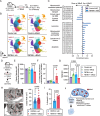
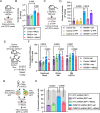
The competitive advantage of mutant hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells (HSPCs) underlies clonal hematopoiesis (CH). Drivers of CH include aging and inflammation; however, how CH-mutant cells gain a selective advantage in these contexts is an unresolved question. Using a murine model of CH (Dnmt3aR878H/+), we discover that mutant HSPCs sustain elevated mitochondrial respiration which is associated with their resistance to aging-related changes in the bone marrow microenvironment. Mutant HSPCs have DNA hypomethylation and increased expression of oxidative phosphorylation gene signatures, increased functional oxidative phosphorylation capacity, high mitochondrial membrane potential (Δψm), and greater dependence on mitochondrial respiration compared to wild-type HSPCs. Exploiting the elevated Δψm of mutant HSPCs, long-chain alkyl-TPP molecules (MitoQ, d-TPP) selectively accumulate in the mitochondria and cause reduced mitochondrial respiration, mitochondrial-driven apoptosis and ablate the competitive advantage of HSPCs ex vivo and in vivo in aged recipient mice. Further, MitoQ targets elevated mitochondrial respiration and the selective advantage of human DNMT3A-knockdown HSPCs, supporting species conservation. These data suggest that mitochondrial activity is a targetable mechanism by which CH-mutant HSPCs gain a selective advantage over wild-type HSPCs.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: A.D.S. has received research funding from Takeda Pharmaceuticals, BMS and Medivir AB, and consulting fees/honorarium from Takeda, Novartis, Jazz, and Otsuka Pharmaceuticals. A.D.S. is named on a patent application for the use of DNT cells to treat AML. A.D.S. is a member of the Medical and Scientific Advisory Board of the Leukemia and Lymphoma Society of Canada. S.M.C. has received research funding from the Centre for Oncology and Immunology in Hong Kong, Celgene/BMS, AbbVie Pharmaceuticals, Agios Pharmaceuticals, and Servier Laboratories. M.R.M. is on the Scientific Advisory Board for Peptone and performed consultancy for Nuage Therapeutics. G.A.C. has performed consulting and received research funding from Incyte, Ajax Therapeutics and ReNAgade Therapeutics Management, and is a co-founder, member of the scientific advisory board and shareholder of Pairidex, Inc. J.J.T. has received research funding from H3 Biomedicine, Inc and patent royalties from Fate Therapeutics. The remaining authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01AG069010/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute on Aging (U.S. National Institute on Aging)
- R01DK118072/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (National Institute of Diabetes & Digestive & Kidney Diseases)
- U01AG077925/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute on Aging (U.S. National Institute on Aging)
- R01 DK124883/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK098263/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA034196/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01DK098263/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (National Institute of Diabetes & Digestive & Kidney Diseases)
- R56DK118072/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (National Institute of Diabetes & Digestive & Kidney Diseases)
- R01 HL148852/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30CA034196/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Cancer Institute (NCI)
- R01 DK118072/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD016214/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R01DK124883/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (National Institute of Diabetes & Digestive & Kidney Diseases)
- R01 AG069010/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R56 DK118072/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG077925/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK119394/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01HL148852/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI)
- R01DK119394/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (National Institute of Diabetes & Digestive & Kidney Diseases)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

