Use of the Malaria Protein VAR2CSA for the Detection of Small Extracellular Vesicles to Diagnose Adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 40241173
- PMCID: PMC12003099
- DOI: 10.1002/jev2.70067
Use of the Malaria Protein VAR2CSA for the Detection of Small Extracellular Vesicles to Diagnose Adenocarcinoma
Abstract
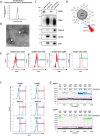
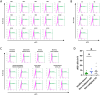
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) poses a significant challenge for early diagnosis due to the lack of sensitive and specific biomarkers. This encouraged us to explore the diagnostic value of cancer-derived small extracellular vesicles (sEVs) as early detection biomarkers. We previously showed that the recombinant malaria protein VAR2CSA (rVAR2) selectively binds to oncofetal chondroitin sulfate (ofCS) on the surfaces of cancer cells, which might be useful for identifying cancer-derived sEVs. Indeed, flow cytometry revealed strong ofCS expression in PDAC cell-derived sEVs, as evidenced by the presence of mutant KRAS, a common genetic alteration in PDAC. Plasma from PDAC patients showed significantly higher ofCS+ sEV levels compared to healthy donors and patients with benign gastrointestinal diseases. ROC analysis for ofCS+ sEVs revealed an AUC of 0.9049 for the detection of all-stage and 0.9222 for early-stage PDAC. Notably, mutant KRAS was also detected in these patient-derived sEVs. Most intriguingly, combining ofCS+ sEVs and CA19-9 resulted in an AUC of 0.9707 for the detection of early PDAC. Our study demonstrates that rVAR2 is suitable for detecting ofCS+ cancer-derived sEVs in plasma, thereby providing high efficiency for identifying PDAC patients among a diverse population. These findings suggest that rVAR2-based sEV detection could serve as a powerful diagnostic tool to improve patient survival through early detection.
Keywords: Early diagnosis; extracellular vesicles; oncofetal chondroitin sulfate; pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma; recombinant malaria protein.
© 2025 The Author(s). Journal of Extracellular Vesicles published by Wiley Periodicals, LLC on behalf of the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles.
Conflict of interest statement
M.Ø.A., T.M.C. T.G.T. and A.S. are shareholders in VAR2 Pharma ApS holding a patent on utilising rVAR2 for diagnosing cancer and were not involved in the data analysis. All other authors have no conflict of interest to disclose.
Figures



References
-
- Allenson, K. , Castillo J., San Lucas F. A., et al. 2019. “Pancreatic Cancer Screening: More Harms Than Benefits?” Lancet Gastroenterology & Hepatology 28, no. 4: 741–747. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- MOST 111-2314-B-039-056/Ministry of Science and Technology, Taiwan
- NSTC 113-2314-B-039-073-MY3/Ministry of Science and Technology, Taiwan
- Pa-CSC 233460/H2020 European Research Council
- 82130074/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82250710179/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 602783/FP7 Ideas: European Research Council
- 2021-01-07-00-02-E00090;21PJ1408900/Shanghai Municipal Education Commission
- NNF21OC0068192/National Nordic Foundation
- NNF22OC0076055/National Nordic Foundation
- IG 2023 ID 28933/Fondazione AIRC per la ricerca sul cancro ETS
- 21PJ1408900/Shanghai Pujiang Program
- PTCRC-Intra-2021ADVANCE/Fondazione del Piemonte per l'Oncologia
- PTCRC-Intra-2024CARESS/Fondazione del Piemonte per l'Oncologia
- 114741/Eurostars
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

