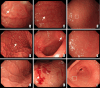
[Diagnostic value of endoscopic findings under white light gastroscopy for Helicobacter pylori infection in children]
- PMID: 40241362
- PMCID: PMC12011010
- DOI: 10.7499/j.issn.1008-8830.2411069
[Diagnostic value of endoscopic findings under white light gastroscopy for Helicobacter pylori infection in children]
Abstract
Objectives: To explore the clinical value of endoscopic findings under white light gastroscopy in diagnosing Helicobacter pylori (Hp) infection in children.
Methods: A retrospective analysis was conducted on the clinical data of 340 children who underwent gastroscopy and gastric mucosa tissue Hp culture from July 2022 to June 2023 in the Department of Gastroenterology at Wuxi Children's Hospital due to upper gastrointestinal symptoms. Based on the results of Hp culture, the children were categorized into an Hp-infected group (146 cases) and a non-infected group (194 cases). The detection rates of various endoscopic findings in the gastric mucosa between the two groups were compared, and the association between each endoscopic finding and different Hp infection statuses was analyzed, as well as the diagnostic value of each endoscopic finding under different Hp infection statuses.
Results: The proportions of white mucus, diffuse redness, mucosal edema, enlarged folds, chicken skin-like changes, and ulcers in the Hp-infected group were higher than those in the non-infected group (P<0.05), while the proportions of regular arrangement of collecting venules (RAC) and ridge-like redness were lower in the Hp-infected group compared to the non-infected group (P<0.05). Multivariate logistic regression analysis showed that diffuse redness, enlarged folds, mucosal edema, and chicken skin-like changes were closely associated with Hp infection (P<0.05), while RAC and ridge-like redness were closely associated with the absence of Hp infection (P<0.05). Receiver operating characteristic curve analysis indicated that the area under the curve for diffuse redness, enlarged folds, mucosal edema, and chicken skin-like changes in predicting Hp infection was 0.798, 0.731, 0.782, and 0.760, respectively (P<0.05). The area under the curve for RAC and ridge-like redness in predicting the absence of Hp infection was 0.861 and 0.589, respectively (P<0.05).
Conclusions: Endoscopic findings under white light gastroscopy are associated with Hp infection in children, with diffuse redness, mucosal edema, chicken skin-like changes, and enlarged folds showing significant diagnostic value for Hp infection.
目的: 探究白光胃镜下内镜征象对诊断儿童幽门螺杆菌(Helicobacter pylori, Hp)感染的临床价值。方法: 回顾性收集2022年7月—2023年6月因上消化道相关症状在无锡市儿童医院消化内科同时行胃镜检查和胃黏膜组织Hp培养检查的340例患儿的临床资料,根据Hp培养结果分为Hp感染组(146例)和Hp未感染组(194例)。比较两组胃黏膜不同内镜征象的检出率,分析各内镜征象与不同Hp感染状态的关联,并比较不同Hp感染状态下各内镜征象的诊断价值。结果: Hp感染组白色黏液、弥漫性发红、黏膜水肿、皱襞肿大、鸡皮样变、溃疡的比例高于Hp未感染组(P<0.05),规则排列的集合细静脉(regular arrangement of collecting venules, RAC)、脊状发红的比例低于Hp未感染组(P<0.05)。多因素logistic回归分析显示,弥漫性发红、皱襞肿大、黏膜水肿、鸡皮样变与Hp感染密切相关(P<0.05),RAC、脊状发红与Hp未感染密切相关(P<0.05)。受试者操作特征曲线分析显示,弥漫性发红、皱襞肿大、黏膜水肿、鸡皮样变预测Hp感染的曲线下面积分别为0.798、0.731、0.782、0.760(P<0.05)。RAC、脊状发红预测Hp未感染的曲线下面积分别为0.861、0.589(P<0.05)。结论: 白光胃镜下内镜征象与儿童Hp感染具有关联性,其中弥漫性发红、黏膜水肿、鸡皮样变、皱襞肿大对Hp感染的诊断价值较高。.
Keywords: Child; Endoscopic finding; Helicobacter pylori; White light gastroscopy.
Conflict of interest statement
所有作者均声明无利益冲突。
Figures
Similar articles
-
Diagnosis by combination of endoscopic findings helps differentiate non-Helicobacter pylori Helicobacter-infected gastritis from Helicobacter pylori-infected gastritis.Helicobacter. 2024 Mar-Apr;29(2):e13070. doi: 10.1111/hel.13070. Helicobacter. 2024. PMID: 38514917
-
Establishment of a modified Kyoto classification scoring model and its significance in the diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori current infection.Gastrointest Endosc. 2023 Apr;97(4):684-693. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2022.11.008. Epub 2022 Nov 18. Gastrointest Endosc. 2023. PMID: 36403805
-
Validity of endoscopic features for the diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori infection status based on the Kyoto classification of gastritis.Dig Endosc. 2020 Jan;32(1):74-83. doi: 10.1111/den.13486. Epub 2019 Sep 26. Dig Endosc. 2020. PMID: 31309632
-
Endoscopic Kyoto classification of Helicobacter pylori infection and gastric cancer risk diagnosis.World J Gastroenterol. 2020 Feb 7;26(5):466-477. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i5.466. World J Gastroenterol. 2020. PMID: 32089624 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characteristic endoscopic findings in Helicobacter pylori diagnosis in clinical practice.Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024 Aug;18(8):457-472. doi: 10.1080/17474124.2024.2395317. Epub 2024 Aug 22. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024. PMID: 39162811 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous