Proximal tubule pannexin 1 contributes to mitochondrial dysfunction and cell death during acute kidney injury
- PMID: 40241514
- PMCID: PMC12281490
- DOI: 10.1152/ajprenal.00226.2024
Proximal tubule pannexin 1 contributes to mitochondrial dysfunction and cell death during acute kidney injury
Abstract
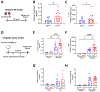
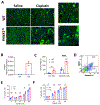
Pannexin 1 (Panx1) is a membrane-associated channel that, when activated, facilitates the release of small metabolites into the extracellular environment. These metabolites signal as damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMP) and initiate inflammation. Upregulation and activation of Panx1 is one of the early events during inflammatory injury. Animal models show that a lack of Panx1 is protective against acute kidney injury (AKI). How Panx1 modulates AKI is poorly understood. We utilized both in vivo and in vitro models of PANX1 overexpression to study mitochondrial function, cell death, and inflammation to evaluate how Panx1 contributes to AKI. We used two models of AKI, ischemia-reperfusion injury (IRI) and cisplatin-induced AKI (cis-AKI), in animals that overexpress PANX1 globally or specifically in the proximal tubule or in the endothelium. Cisplatin-induced injury was investigated in vitro in PANX1-overexpressing proximal tubule cells in culture. Both global and proximal tubule-specific overexpression of PANX1 exacerbated AKI, whereas endothelium-specific overexpression had no effect. Panx1-dependent metabolite release and alterations in the intracellular compartment in proximal tubules independently contributed to cell death in vitro. PANX1 overexpression impaired mitochondrial function and increased mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (ROS) production. PANX1 overexpression resulted in increased inflammation in the kidneys during cis-AKI. We showed that PANX1 overexpression resulted in overt renal injury during AKI that is in part mediated by reduced mitochondrial function, increased cell death, and inflammation. Selective strategies to inhibit Panx1 could help prevent or treat AKI.NEW & NOTEWORTHY Despite the huge medical, economical, and quality of life burden that AKI poses to patients, there are no Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-approved therapeutic or pharmaceutical interventions for AKI. Pannexin 1 (Panx1), which is upregulated in patients with AKI as well as in animals that develop experimental AKI, plays a crucial role in mediating both inflammation and cell death during AKI. Our findings suggest clinical interventions with molecules that inhibit Panx1 channel activity could improve outcomes in AKI patients.
Keywords: ATP; acute kidney injury; cell death; mitochondria; pannexins.
Conflict of interest statement
DISCLOSURES
All the authors declared no competing interests.
Figures






References
-
- Baranova A, Ivanov D, Petrash N, Pestova A, Skoblov M, Kelmanson I, Shagin D, Nazarenko S, Geraymovych E, Litvin O, Tiunova A, Born TL, Usman N, Staroverov D, Lukyanov S, Panchin Y. The mammalian pannexin family is homologous to the invertebrate innexin gap junction proteins. Genomics 83: 706–716, 2004. doi: 10.1016/j.ygeno.2003.09.025. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chekeni FB, Elliott MR, Sandilos JK, Walk SF, Kinchen JM, Lazarowski ER, Armstrong AJ, Penuela S, Laird DW, Salvesen GS, Isakson BE, Bayliss DA, Ravichandran KS. Pannexin 1 channels mediate ‘find-me’ signal release and membrane permeability during apoptosis. Nature 467: 863–867, 2010. doi: 10.1038/nature09413. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Good ME, Eucker SA, Li J, Bacon HM, Lang SM, Butcher JT, Johnson TJ, Gaykema RP, Patel MK, Zuo Z, Isakson BE. Endothelial cell Pannexin1 modulates severity of ischemic stroke by regulating cerebral inflammation and myogenic tone. JCI Insight 3, 2018. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.96272. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- AI139763/HHS | NIH | NIAID | Division of Intramural Research (DIR, NIAID)
- R01 DK123248/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK133097/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK085259/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 1S10RR026799-01/HHS | NIH | Office of Research Infrastructure Programs (ORIP)
- U01 DK114933/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK114908/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK133095/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32GM007267/HHS | NIH | National Institute of General Medical Sciences (NIGMS)
- U01 DK114920/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U24 DK114886/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK133766/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007267/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- DK085259/HHS | NIH | National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK)
- DK123248/HHS | NIH | National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK)
- Ben J Lipps Fellowship/ASN Foundation for Kidney Research (ASN Foundation)
- U01 DK114923/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK133113/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL120840/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK114866/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK133090/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UH3 DK114915/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK133768/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK133092/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UH3 DK114861/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI139673/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UH3 DK114937/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK133081/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UH3 DK114926/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- S10 RR026799/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK114907/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK133091/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK133093/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

