Enhancing Specificity in Predicting Axillary Lymph Node Metastasis in Breast Cancer through an Interpretable Machine Learning Model with CEM and Ultrasound Integration
- PMID: 40241520
- PMCID: PMC12035205
- DOI: 10.1177/15330338251334735
Enhancing Specificity in Predicting Axillary Lymph Node Metastasis in Breast Cancer through an Interpretable Machine Learning Model with CEM and Ultrasound Integration
Abstract
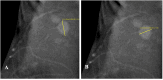
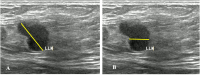
IntroductionThe study aims to evaluate the performance of an interpretable machine learning model in predicting preoperative axillary lymph node metastasis using primary breast cancer and lymph node features derived from contrast-enhanced mammography (CEM) and ultrasound (US) breast imaging reporting and data systems (BI-RADS).MethodsThis retrospective study included patients diagnosed with primary breast cancer. Two experienced radiologists extracted the BI-RADS features from the largest cross-section of the lesions and axillary lymph nodes based on CEM and US images, creating three datasets. Each dataset will train six base models to predict axillary lymph nodes, with pathological results serving as the gold standard. The top three models were used to train the five ensemble models. Additionally, SHapley Additive exPlanations (SHAP) was used to interpret the optimal model. The receiver-operating characteristic curve (ROC) and AUC were used to evaluate model performance.ResultsThis study involved 292 female patients, of whom 99 had axillary lymph node metastasis and 193 did not. The combination of CEM and ultrasound BI-RADS demonstrated the best performance in predicting axillary lymph node metastasis. Among these, the LightGBM achieved the highest AUC (0.762) and specificity (86.67%, while the ensemble model using RF as the meta-model had an AUC (0.754) and specificity (83.33%. The most important variables identified by SHAP were the long diameters of the lymph nodes in the CEM recombined image, along with their complete morphology in the low-energy image.ConclusionThe machine learning model using CEM and US BI-RADS features accurately predicted axillary lymph node metastasis before surgery, thereby serving as a valuable tool for clinical decision-making in patients with breast cancer.
Keywords: CEM; axillary lymph node metastasis; breast cancer; machine learning; ultrasound.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicting InterestsThe authors declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures



References
-
- Bray F, Laversanne M, Sung H, et al. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2024;74(3):229-263. - PubMed
-
- Schröder L, Fricker R, Stein RG, et al. Evaluation of sentinel lymph node biopsy prior to axillary lymph node dissection: The role of isolated tumor cells/micrometastases and multifocality/multicentricity—a retrospective study of 1214 breast cancer patients. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2018;297(6):1509-1515. - PubMed
-
- Alvarez S, Añorbe E, Alcorta P, et al. Role of sonography in the diagnosis of axillary lymph node metastases in breast cancer: A systematic review. Am J Roentgenol. 2006;186(5):1342-1348. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

