A phase I/IIa trial of PXS-5505, a novel pan-lysyl oxidase inhibitor, in advanced myelofibrosis
- PMID: 40241543
- PMCID: PMC12485312
- DOI: 10.3324/haematol.2024.287231
A phase I/IIa trial of PXS-5505, a novel pan-lysyl oxidase inhibitor, in advanced myelofibrosis
Abstract
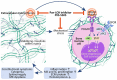
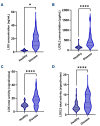
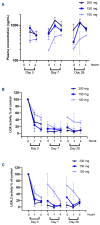
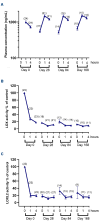
Myelofibrosis is a progressive disease characterized by accumulation of extracellular matrix in the bone marrow (BM), which impairs normal hematopoiesis. While Janus kinase inhibitors reduce spleen volume and provide symptomatic improvement, they do not resolve BM fibrosis and may cause or exacerbate anemia and thrombocytopenia. An antifibrotic therapy capable of normalizing the BM microenvironment and function remains a significant gap in the current treatment landscape. Myelofibrosis is associated with elevated expression of lysyl oxidases, enzymes responsible for maturation of the most abundant extracellular matrix proteins: collagen and elastin. PXS-5505 is a novel pan-lysyl oxidase inhibitor designed to exert an antifibrotic effect by preventing the cross-linking of collagen and elastin. PXS5505-MF-101 is a multicenter phase I/IIa study of PXS-5505 in myelofibrosis patients which included a dose escalation phase (DEP) and a cohort expansion phase (CEP). Primary objectives of the study were to determine the safety and tolerability of PXS-5505 and to define dosing for future studies. The DEP demonstrated that the highest dose tested, 200 mg BID, was safe and achieved robust systemic reduction of lysyl oxidase activity; this dose was, therefore, selected for the CEP. Twenty-four patients (median age 72 years) with relapsed or refractory myelofibrosis were recruited into the CEP and 54% (13/24) completed 24 weeks of treatment. PXS-5505 was well tolerated and reached steady-state concentrations by day 28. Over the 24-week treatment period preliminary indications of clinical efficacy, including a reduction in BM collagen, were evident. Overall, these data support continued investigation of PXS-5505. (ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT04676529).
Figures

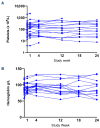
References
-
- Tefferi A. Primary myelofibrosis: 2023 update on diagnosis, risk-stratification, and management. Am J Hematol. 2023;98(5):801-821. - PubMed
-
- Tadmor T, Bejar J, Attias D, et al. The expression of lysyl-oxidase gene family members in myeloproliferative neoplasms. Am J Hematol. 2013;88(5):355-358. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

