Mechanical control of the alternative splicing factor PTBP1 regulates extracellular matrix stiffness induced proliferation and cell spreading
- PMID: 40241749
- PMCID: PMC12002664
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2025.112273
Mechanical control of the alternative splicing factor PTBP1 regulates extracellular matrix stiffness induced proliferation and cell spreading
Abstract
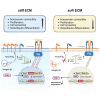
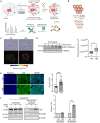
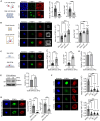
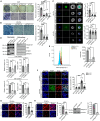
Cells sense mechanical cues and convert them into biochemical responses to regulate biological processes such as embryonic development, aging, cellular homeostasis, and disease progression. In this study, we introduce a large-scale, systematic approach to identify proteins with mechanosensitive nuclear localization, highlighting their potential roles in mechanotransduction. Among the proteins identified, we focus here on the splicing factor PTBP1. We demonstrate that its nuclear abundance is regulated by mechanical cues such as cell density, size, and extracellular matrix (ECM) stiffness and that PTBP1 medicates the mechanosensitive alternative splicing of the endocytic adapter protein Numb. Furthermore, we show that PTBP1 and Numb alternative splicing is critical for ECM stiffness-induced epithelial cell spreading and proliferation as well as for mesenchymal stem cell differentiation into osteoblasts on a stiff matrix. Our results underscore the emerging role of alternative splicing in mechanotransduction and provide novel mechanistic insights into how matrix stiffness modulates cellular mechanoresponses.
Keywords: Cell biology; Functional aspects of cell biology; Organizational aspects of cell biology.
© 2025 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Extracellular matrix type modulates mechanotransduction of stem cells.Acta Biomater. 2019 Sep 15;96:310-320. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2019.06.048. Epub 2019 Jun 28. Acta Biomater. 2019. PMID: 31255664 Free PMC article.
-
Energy expenditure during cell spreading influences the cellular response to matrix stiffness.Biomaterials. 2021 Jan;267:120494. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2020.120494. Epub 2020 Oct 24. Biomaterials. 2021. PMID: 33130323
-
PTBP1 crotonylation promotes colorectal cancer progression through alternative splicing-mediated upregulation of the PKM2 gene.J Transl Med. 2024 Nov 4;22(1):995. doi: 10.1186/s12967-024-05793-5. J Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 39497094 Free PMC article.
-
Cell-extracellular matrix mechanotransduction in 3D.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2023 Jul;24(7):495-516. doi: 10.1038/s41580-023-00583-1. Epub 2023 Feb 27. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2023. PMID: 36849594 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Roles of PTBP1 in alternative splicing, glycolysis, and oncogensis.J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2020 Feb.;21(2):122-136. doi: 10.1631/jzus.B1900422. Epub 2020 Feb 5. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2020. PMID: 32115910 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Elosegui-Artola A., Andreu I., Beedle A.E.M., Lezamiz A., Uroz M., Kosmalska A.J., Oria R., Kechagia J.Z., Rico-Lastres P., Le Roux A.L., et al. Force Triggers YAP Nuclear Entry by Regulating Transport across Nuclear Pores. Cell. 2017;171:1397–1410.e14. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.10.008. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

