Effects of the subanesthetic dose of esketamine on postoperative sleep quality in patients undergoing modified radical mastectomy: a randomized, double-blind controlled trial
- PMID: 40241908
- PMCID: PMC12000102
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1552934
Effects of the subanesthetic dose of esketamine on postoperative sleep quality in patients undergoing modified radical mastectomy: a randomized, double-blind controlled trial
Abstract
Background: Breast cancer is the most common malignant tumor among women worldwide. Surgical intervention is a critical component of treatment, yet the associated stress and anxiety can significantly disrupt postoperative sleep quality. Emerging evidences suggest that esketamine may offer benefits in alleviating emotional distress and enhancing sleep. The purpose of this study was to observe the effects of intraoperative subanesthetic dose of esketamine on the sleep of patients undergoing modified radical mastectomy.
Methods: This randomized, double-blind, controlled trial enrolled 145 female patients, who were randomly assigned to either the esketamine group (Group E, n = 72) or the control group (Group C, n = 73). Patients in Group E received esketamine (0.2 mg/kg loading dose, followed by 0.1 mg/kg/h infusion), while those in Group C received saline (0.2 mL/kg loading dose, followed by 0.1 mL/kg/h infusion). The primary outcome was the total score on the Richards-Campbell Sleep Questionnaire (RCSQ) measured on postoperative day (POD) 1. Secondary outcomes included recovery time, the incidence of postoperative adverse events and rescue analgesia, Visual Analogue Scale (VAS) pain scores, short-form McGill's Pain Questionnaire (SF-MPQ) sensory and affective scores, and Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (PSQI) scores.
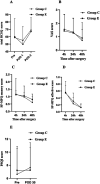
Results: No significant differences were observed in the total RCSQ scores on POD 1 between Group E and Group C (median [interquartile range]: 46 [32-68] vs. 54 [40-71], p > 0.05). Recovery time was significantly longer in Group E compared to Group C (8 [5-11] vs. 6 [4-11] minutes; p = 0.02). There were no significant differences in the incidence of adverse events or remedial analgesia within 48 h postoperatively. Furthermore, no significant differences were observed between the groups in pain VAS scores, and SF-MPQ sensory or affective scores at 4, 24, and 48 h postoperatively. PSQI scores on POD 30 were not significantly different between the groups (p > 0.05).
Conclusion: For female patients without pre-existing sleep disorders undergoing modified radical mastectomy, intraoperative subanesthetic esketamine may not significantly impact postoperative sleep quality but potentially contribute to a prolonged recovery time.
Trial registration: This trial was registered at the Chinese Clinical Trial Registry on July 03, 2022 (https://www.chictr.org.cn; Registration number: ChiCTR2200061818).
Keywords: breast cancer; esketamine; modified radical mastectomy; postoperative sleep disturbance; recovery.
Copyright © 2025 Chen, He, Huang, Pan, Zhong and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Effects of a single subanesthetic dose of esketamine on postoperative subthreshold depressive symptoms in patients undergoing unilateral modified radical mastectomy: a randomised, controlled, double-blind trial.BMC Psychiatry. 2024 Apr 24;24(1):315. doi: 10.1186/s12888-024-05753-9. BMC Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 38658886 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of the Different Doses of Esketamine on Postoperative Quality of Recovery in Patients Undergoing Modified Radical Mastectomy: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Controlled Trial.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2022 Dec 16;16:4291-4299. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S392784. eCollection 2022. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2022. PMID: 36561309 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of sub-anesthetic doses of esketamine on postoperative sleep disturbance and pain in patients undergoing lumbar interbody fusion - A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, two-center trial.Anaesth Crit Care Pain Med. 2025 Jun 14:101567. doi: 10.1016/j.accpm.2025.101567. Online ahead of print. Anaesth Crit Care Pain Med. 2025. PMID: 40523523
-
Esketamine and neurocognitive disorders in adult surgical patients: a meta-analysis.BMC Anesthesiol. 2024 Dec 5;24(1):448. doi: 10.1186/s12871-024-02803-3. BMC Anesthesiol. 2024. PMID: 39639216 Free PMC article.
-
Effect and safety of perioperative ketamine/esketamine administration on postoperative pain and depression after breast cancer surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Mar 28;16:1532524. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1532524. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40223927 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mubarik S, Yu Y, Wang F, Malik SS, Liu X, Fawad M, et al. . Epidemiological and sociodemographic transitions of female breast cancer incidence, death, case fatality and DALYs in 21 world regions and globally, from 1990 to 2017: an age-period-cohort analysis. J Adv Res. (2022) 37:185–96. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2021.07.012, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wang H, Te R, Zhang J, Su Y, Zhou H, Guo N, et al. . Effects of a single subanesthetic dose of esketamine on postoperative subthreshold depressive symptoms in patients undergoing unilateral modified radical mastectomy: a randomised, controlled, double-blind trial. BMC Psychiatry. (2024) 24:315. doi: 10.1186/s12888-024-05753-9, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zhu M, Xu S, Ju X, Wang S, Yu X. Effects of the different doses of Esketamine on postoperative quality of recovery in patients undergoing modified radical mastectomy: a randomized, double-blind, controlled trial. Drug Des Devel Ther. (2022) 16:4291–9. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S392784, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

