Long-term tofacitinib efficacy and safety in psoriatic arthritis with or without prior biologic DMARD exposure: a post hoc analysis
- PMID: 40241921
- PMCID: PMC12002910
- DOI: 10.1093/rap/rkaf008
Long-term tofacitinib efficacy and safety in psoriatic arthritis with or without prior biologic DMARD exposure: a post hoc analysis
Abstract
Objective: To assess long-term tofacitinib efficacy and safety in patients with PsA with or without prior biologic DMARD (bDMARD) exposure.
Methods: Data were pooled post hoc from three phase 3 and one long-term extension (LTE) PsA studies and stratified by TNF inhibitor-inadequate responder (TNFi-IR) or bDMARD-naïve patient status at the phase 3 study baseline. Data were reported as all tofacitinib (patients receiving one or more tofacitinib doses) or average tofacitinib 5 and 10 mg twice daily (patients receiving an average total daily dose <15 and ≥15 mg, respectively). Drug survival to month 51, efficacy to month 42 and safety were assessed descriptively.
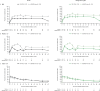
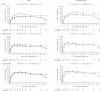
Results: A total of 408 TNFi-IR patients (including 29 TNFi-experienced with unknown IR status) and 562 bDMARD-naïve patients were included. At baseline, TNFi-IR patients were more likely to be ≥65 years old, have cardiovascular/venous thromboembolism risk and have longer disease duration vs bDMARD-naïve patients. Drug survival was numerically shorter in TNFi-IR vs bDMARD-naïve patients. Tofacitinib efficacy was generally sustained to month 42, regardless of prior bDMARD treatment. Minimal disease activity/ PsA Disease Activity Score ≤3.2/>75% Psoriasis Area and Severity Index improvement response rates were numerically lower in TNFi-IR vs bDMARD-naïve patients to month 42, but rates of achieving an HAQ Disability Index ≤0.5 and enthesitis/dactylitis resolution were similar. In TNFi-IR vs bDMARD-naïve patients, treatment-emergent adverse event incidence rates were higher and serious adverse event, serious infection and herpes zoster incidence rates were numerically higher (CI overlapped).
Conclusion: These findings support long-term tofacitinib efficacy and safety in TNFi-IR and bDMARD-naïve patients. However, the benefit-risk profile appeared more favourable in bDMARD-naïve patients, likely due to differences in baseline characteristics and risk factors between subgroups.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov: NCT01877668, NCT01882439, NCT03486457, NCT01976364.
Keywords: JAK inhibitors; biologic therapies; interventional studies; psoriatic arthritis; tofacitinib.
© The Author(s) 2025. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the British Society for Rheumatology.
Figures


References
-
- FitzGerald O, Ogdie A, Chandran V et al. Psoriatic arthritis. Nat Rev Dis Primers 2021;7:59. - PubMed
-
- Kavanaugh A, McInnes IB, Mease PJ et al. Efficacy of subcutaneous secukinumab in patients with active psoriatic arthritis stratified by prior tumor necrosis factor inhibitor use: results from the randomized placebo-controlled FUTURE 2 study. J Rheumatol 2016;43:1713–7. - PubMed
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
