Vitamin D Deficiency and Clinical Outcomes in Critically Ill Pediatric Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 40242208
- PMCID: PMC12001026
- DOI: 10.1210/jendso/bvaf053
Vitamin D Deficiency and Clinical Outcomes in Critically Ill Pediatric Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Context: Vitamin D deficiency (VDD) is common in paediatric populations, and its relationship with critical care outcomes warrants further investigation.
Objective: The aim is to examine the association between VDD and clinical outcomes in children admitted to the Pediatric Intensive Care Unit (PICU).
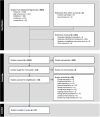
Methods: This systematic review and meta-analysis investigated the impact of VDD on clinical outcomes in PICU patients. A comprehensive search of Embase, Web of Science, PubMed, and Cochrane databases was conducted. Our primary outcomes were mortality and sepsis incidence, while secondary outcomes included length of stay (LOS), need for inotropic support, and need for and duration of mechanical ventilation. Eligible studies included infants and children aged 1 month to 18 years admitted to the PICU, with baseline 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels measured on admission. Two independent reviewers screened studies, extracted data, and assessed quality. Pooled estimates were obtained using a random-effects model.
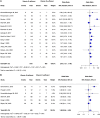
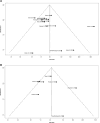
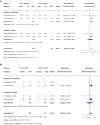
Results: Out of 2298 screened studies, 27 met the inclusion criteria, comprising 4682 patients. VDD was defined as 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels <20 ng/mL and <30 ng/mL in 22 and 5 studies, respectively. VDD was associated with increased mortality (odds ratio [OR] 2.05, 95% CI 1.21-3.48) and a greater need for inotropic support (OR 2.02, 95% CI 1.43-2.85) than children with vitamin D sufficiency (VDS). No differences were observed between VDD and VDS groups in terms of sepsis incidence postadmission, LOS, or the need for and duration of mechanical ventilation.
Conclusion: VDD in critically ill pediatric patients was associated with increased mortality and higher need for inotropic support. Further research is warranted to evaluate the potential benefits of vitamin D supplementation in this high-risk population.
Keywords: critical care outcomes; pediatric intensive care unit; vitamin D.
© The Author(s) 2025. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Endocrine Society.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Vitamin D deficiency in critically ill children with sepsis.Paediatr Int Child Health. 2016 Feb;36(1):15-21. doi: 10.1179/2046905515Y.0000000042. Epub 2015 Jun 27. Paediatr Int Child Health. 2016. PMID: 26120004
-
[Vitamin D deficiency in children admitted to the paediatric intensive care unit].Rev Chil Pediatr. 2016 Nov-Dec;87(6):480-486. doi: 10.1016/j.rchipe.2016.05.008. Epub 2016 Jul 2. Rev Chil Pediatr. 2016. PMID: 27381433 Spanish.
-
Vitamin D deficiency relation to sepsis, paediatric risk of mortality III score, need for ventilation support, length of hospital stay, and duration of mechanical ventilation in critically ill children: A meta-analysis.Int J Clin Pract. 2021 Apr;75(4):e13908. doi: 10.1111/ijcp.13908. Epub 2020 Dec 20. Int J Clin Pract. 2021. PMID: 33280208
-
Vitamin D deficiency and clinical outcomes related to septic shock in children with critical illness: a systematic review.Eur J Clin Nutr. 2019 Aug;73(8):1095-1101. doi: 10.1038/s41430-018-0249-0. Epub 2018 Jul 13. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2019. PMID: 30006615
-
The Effect of Vitamin D Supplementation on Clinical Outcomes for Critically Ill Patients: A Systemic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials.Front Nutr. 2021 May 4;8:664940. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2021.664940. eCollection 2021. Front Nutr. 2021. PMID: 34017850 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bustos BR, Rodríguez-Nuñez I, Peña Zavala R, Soto Germani G. Vitamin D deficiency in children admitted to the paediatric intensive care unit. Rev Chil Pediatr. 2016;87(6):480‐486. - PubMed
-
- Al-Matary A, AlMalki Y, Khalil S, AlHulaimi E. The potential effects of vitamin D deficiency on respiratory distress syndrome among preterm infants. Clin Nutr ESPEN. 2021;44:243‐246. - PubMed
-
- Wang Y, Shi C, Yang Z, Chen F, Gao L. Vitamin D deficiency and clinical outcomes related to septic shock in children with critical illness: a systematic review. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2019;73(8):1095‐1101. - PubMed
-
- Ebenezer K, Job V, Antonisamy B, Dawodu A, Manivachagan MN, Steinhoff M. Serum vitamin D status and outcome among critically ill children admitted to the pediatric intensive care unit in south India. Indian J Pediatr. 2016;83(2):120‐125. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
