Palmitoylation in cardiovascular diseases: Molecular mechanism and therapeutic potential
- PMID: 40242212
- PMCID: PMC12002947
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijcha.2025.101675
Palmitoylation in cardiovascular diseases: Molecular mechanism and therapeutic potential
Abstract
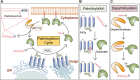
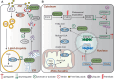
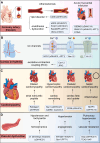
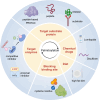
Cardiovascular disease is one of the leading causes of mortality worldwide, and involves complex pathophysiological mechanisms that encompass various biological processes and molecular pathways. Post-translational modifications of proteins play crucial roles in the occurrence and progression of cardiovascular diseases, among which palmitoylation is particularly important. Various proteins associated with cardiovascular diseases can be palmitoylated to enhance the hydrophobicity of their molecular subdomains. This lipidation can significantly affect some pathophysiological processes, such as metabolism, inflammation by altering protein stability, localization, and signal transduction. In this review, we narratively summarize recent advances in the palmitoylation of proteins related to cardiovascular diseases and discuss its potential as a therapeutic target.
Keywords: Cardiovascular diseases; Palmitoylation; Post-translational modifications; zDHHC.
© 2025 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Protein palmitoylation: biological functions, disease, and therapeutic targets.MedComm (2020). 2025 Feb 21;6(3):e70096. doi: 10.1002/mco2.70096. eCollection 2025 Mar. MedComm (2020). 2025. PMID: 39991624 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protein palmitoylation in cancer: molecular functions and therapeutic potential.Mol Oncol. 2023 Jan;17(1):3-26. doi: 10.1002/1878-0261.13308. Epub 2022 Sep 10. Mol Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36018061 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protein lipidation in the tumor microenvironment: enzymology, signaling pathways, and therapeutics.Mol Cancer. 2025 May 7;24(1):138. doi: 10.1186/s12943-025-02309-7. Mol Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40335986 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protein Palmitoylation Modification During Viral Infection and Detection Methods of Palmitoylated Proteins.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022 Jan 27;12:821596. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.821596. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35155279 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protein Lipidation by Palmitoylation and Myristoylation in Cancer.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 May 20;9:673647. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.673647. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34095144 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Research trends of protein palmitoylation in cancer from 2004 to 2024: a bibliometric and visualization analysis.Front Oncol. 2025 Jun 23;15:1571870. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1571870. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40626019 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zhao D., et al. Epidemiology of cardiovascular disease in China: current features and implications. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2019;16(4):203–212. - PubMed
-
- Jurgens C.Y., et al. State of the science: the relevance of symptoms in cardiovascular disease and research: a scientific statement from the american heart association. Circulation. 2022;146(12):e173–e184. - PubMed
-
- Dehghan M., et al. Associations of fats and carbohydrate intake with cardiovascular disease and mortality in 18 countries from five continents (PURE): a prospective cohort study. Lancet. 2017;390(10107):2050–2062. - PubMed
-
- Yang M., Zhang Y., Ren J. Acetylation in cardiovascular diseases: Molecular mechanisms and clinical implications. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. basis Dis. 2020;1866(10) - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

