Energy efficiency in ROS communication: a comparison across programming languages and workloads
- PMID: 40242513
- PMCID: PMC11999854
- DOI: 10.3389/frobt.2025.1548250
Energy efficiency in ROS communication: a comparison across programming languages and workloads
Abstract
Introduction: The Robot Operating System (ROS) is a widely used framework for robotic software development, providing robust client libraries for both C++ and Python. These languages, with their differing levels of abstraction, exhibit distinct resource usage patterns, including power and energy consumption-an increasingly critical quality metric in robotics.
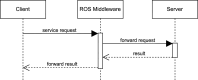
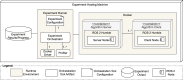
Methods: In this study, we evaluate the energy efficiency of ROS two nodes implemented in C++ and Python, focusing on the primary ROS communication paradigms: topics, services, and actions. Through a series of empirical experiments, with programming language, message interval, and number of clients as independent variables, we analyze the impact on energy efficiency across implementations of the three paradigms.
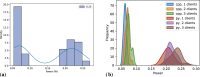
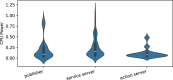
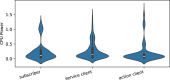
Results: Our data analysis demonstrates that Python consistently demands more computational resources, leading to higher power consumption compared to C++. Furthermore, we find that message frequency is a highly influential factor, while the number of clients has a more variable and less significant effect on resource usage, despite revealing unexpected architectural behaviors of underlying programming and communication layers.
Keywords: ROS; ROS communication; energy efficiency; programming language; robotic.
Copyright © 2025 Albonico, Cannizza and Wortmann.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures









References
-
- Abdi H., Williams L. J. (2010). Tukey’s honestly significant difference (HSD) test. Encycl. Res. Des. 3 (1), 1–5.
-
- Abdulsalam S., Lakomski D., Gu Q., Jin T., Zong Z. (2014). “Program energy efficiency: the impact of language, compiler and implementation choices,” in International green computing conference (IEEE; ), 1–6.
-
- Albonico M., Junior Varela P., Jose Rohling A., Wortmann A. (2024). Energy efficiency of ROS nodes in different languages: publisher/subscriber case studies (RoSE ’24) . New York, NY, USA: Association for Computing Machinery, 1–8. 10.1145/3643663.3643963 - DOI
-
- Basili V., Caldiera G., Rombach H. D. (1994). The goal question metric approach. Encycl. Softw. Eng., 528–532.
-
- Bernard L. W. (1951). On the comparison of several mean values: an alternative approach. Biometrika 38 (3/4), 330–336. 10.2307/2332579 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

