Retime-mapping terahertz vernier biosensor for boosting sensitivity based on self-reference waveguide interferometers
- PMID: 40242530
- PMCID: PMC11997581
- DOI: 10.1016/j.fmre.2024.12.002
Retime-mapping terahertz vernier biosensor for boosting sensitivity based on self-reference waveguide interferometers
Abstract
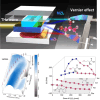
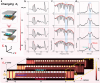
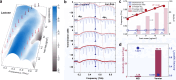
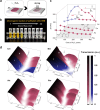
The optical vernier effect serves as a potent mechanism for boosting sensitivity and accuracy in the communication band, which is a prominent hotspot in coherent detection. Extending vernier gain to the terahertz window exhibits significant appeal in next-generation wireless communication and high-resolution sensing. Here, a terahertz vernier biosensor is constructed utilizing two overlapping Mach-Zehnder interferometers within a three-channel metallic waveguide. The self-reference feature of the vernier biosensor facilitates a sensitive envelope, and the vernier gain significantly amplifies the detection sensitivity and accuracy from the superposition of slightly detuned terahertz interference spectra mapping within the time-frequency-time domain. An exalting sensitivity of 22.54 THz/RIU is demonstrated at operating frequencies near 0.9 THz and experimentally shows immense sensing performance in detection sensitivity and accuracy of biochemical sample areic mass are 107 GHz/(g/mm2) and 10-8 g/mm2, respectively, presenting an enhancement of > 3000% compared to a single interferometer. Moreover, the sensor is employed to assess the amino acid oxidation characteristic curve analysis in the terahertz range, which assists in identifying specific amino acids. The validation of the vernier effect operating in the terahertz regime demonstrates the development of a rapid and label-free assistance tool for the identification of biochemical samples.
Keywords: Self-reference detection; Sensitivity enhancement; Terahertz; Vernier biosensor; Waveguide interferometer.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Signal processing assisted Vernier effect in a single interferometer for sensitivity magnification.Opt Express. 2021 Apr 12;29(8):11570-11581. doi: 10.1364/OE.418783. Opt Express. 2021. PMID: 33984934
-
Semiconductor-based plasmonic interferometers for ultrasensitive sensing in a terahertz regime.Opt Lett. 2017 Jun 15;42(12):2338-2341. doi: 10.1364/OL.42.002338. Opt Lett. 2017. PMID: 28614346
-
Optical Harmonic Vernier Effect: A New Tool for High Performance Interferometric Fibre Sensors.Sensors (Basel). 2019 Dec 9;19(24):5431. doi: 10.3390/s19245431. Sensors (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31835433 Free PMC article.
-
Recent advances in gas and chemical detection by Vernier effect-based photonic sensors.Sensors (Basel). 2014 Mar 10;14(3):4831-55. doi: 10.3390/s140304831. Sensors (Basel). 2014. PMID: 24618728 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advanced Fiber Sensors Based on the Vernier Effect.Sensors (Basel). 2022 Mar 31;22(7):2694. doi: 10.3390/s22072694. Sensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35408310 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Label-free sensing technology of two Staphylococcus species based on a terahertz metasurface.Biomed Opt Express. 2025 May 2;16(6):2210-2216. doi: 10.1364/BOE.560412. eCollection 2025 Jun 1. Biomed Opt Express. 2025. PMID: 40677389 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging terahertz sciences and technologies.Fundam Res. 2024 Dec 18;5(2):514-515. doi: 10.1016/j.fmre.2024.12.003. eCollection 2025 Mar. Fundam Res. 2024. PMID: 40242520 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Gomes A.D., Bartelt H., Frazao O. Optical vernier effect: recent advances and developments. Laser Photon. Rev. 2021;15(7)
-
- Riemensberger J., Lukashchuk A., Karpov M., et al. Massively parallel coherent laser ranging using a soliton microcomb. Nature. 2020;581(7807):164–170. - PubMed
-
- Kaur B., Kumar S., Kaushik B.K. Recent advancements in optical biosensors for cancer detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022;197 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

