Harmine hydrochloride induces G0/G1 cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in oral squamous carcinoma cells
- PMID: 40242602
- PMCID: PMC12001316
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2025.12861
Harmine hydrochloride induces G0/G1 cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in oral squamous carcinoma cells
Abstract
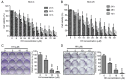
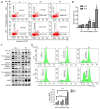
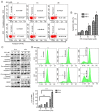
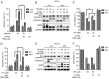
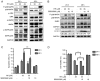
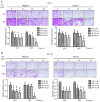
Oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) represents the most frequently occurring form of oral cancer. However, despite the availability of advanced treatment modalities, the global 5-year survival rate for patients with advanced OSCC remains at ~50-60%. Devising alternative therapeutic strategies for oral cancer has therefore become an urgent need. Harmine, a β-carboline alkaloid, has recently been shown to exhibit anticancer activity. Compared with harmine, harmine hydrochloride (HH), a derivative of harmine, has improved water solubility and stability, so can absorb into tissues more readily. Therefore, the present study aimed to investigate the anticancer activity of HH in OSCC cells. A Cell Counting Kit-8 assay was performed to assess the cytotoxic effects of HH on the OSCC cell lines, SCC-4 and SCC-25. Flow cytometric analysis was subsequently employed to examine both the cell cycle profile and the extent of apoptosis. Western blotting was used to assess the expression levels of the regulatory proteins involved in these biological activities, and treatment with a pan-caspase inhibitor (Z-VAD-FMK) confirmed the involvement of the apoptotic pathway. Furthermore, western blotting was used to investigate which signaling pathways were affected in the HH-treated cells. Taken together, the findings of the present study demonstrated that HH was cytotoxic in OSCC cells. HH treatment induced G0/G1 phase cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. Additionally, the MAPK pathway was shown to be involved in HH-induced apoptosis in SCC-4 cells. Therefore, HH exhibited anticancer activity, and may be a putative therapeutic agent for the treatment of OSCC in the future.
Keywords: antitumor activity; apoptosis; harmine hydrochloride; oral squamous cell carcinoma.
Copyright: © 2025 Lin et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Pekarek L, Garrido-Gil MJ, Sánchez-Cendra A, Cassinello J, Pekarek T, Fraile-Martinez O, García-Montero C, Lopez-Gonzalez L, Rios-Parra A, Álvarez-Mon M, et al. Emerging histological and serological biomarkers in oral squamous cell carcinoma: Applications in diagnosis, prognosis evaluation and personalized therapeutics (Review) Oncol Rep. 2023;50(213) doi: 10.3892/or.2023.8650. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
