Green Synthesis and Characterization of Silver Nanoparticles Using Anchusa Officinalis: Antimicrobial and Cytotoxic Potential
- PMID: 40242607
- PMCID: PMC12002332
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S511217
Green Synthesis and Characterization of Silver Nanoparticles Using Anchusa Officinalis: Antimicrobial and Cytotoxic Potential
Abstract
Objective: Anchusa officinalis L. (A. officinalis) is a herbaceous traditional medicinal plant used in the treatment of some diseases. The presence of its medicinal properties suggested that A. officinalis (AO) leaf extract could be used as a coating agent for the environmentally friendly production of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs).
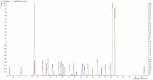
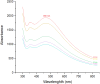
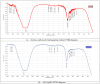
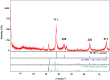
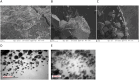
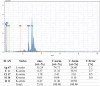
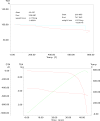
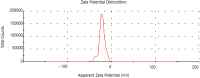
Methods: The synthesized biogenic silver nanoparticles (AO-AgNPs) were characterized using different techniques. The antimicrobial activity of AgNPs against common bacterial pathogenic strains was determined by the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) method. The presence of phytochemicals was determined by LSMS/MS. The MTT assay was used to investigate AO-AgNPs' cytotoxic activity in malignant (LnCap, Caco2, MDA-MB2, A549) and healthy (HEK-293) cell lines.
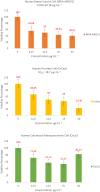
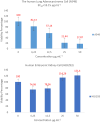
Results: LC-MS/MS analysis detected the presence of rich phytochemicals that may be responsible for reduction reactions. Biogenic AO-AgNPs exhibited effective inhibition of the growth of pathogenic microorganisms at low concentrations. The most effective antimicrobial activity was measured as 0.5 µg/mL MIC against S. aureus, E. coli, and C. albicans. Moreover, AO-AgNPs showed significant inhibition on the growth of cancerous cell lines, especially at a concentration of 25 μg/mL. On the contrary, it was determined that the inhibition rate decreased in the growth of healthy cell lines due to the increase in concentration. The lowest EC50 values were determined as 15.15 µg/mL in A549 cells.
Conclusion: The obtained results showed that AO could be an important source for the synthesis of AgNPs. Especially their ability to inhibit the growth of antibiotic-resistant pathogenic bacteria at low concentrations compared to common antibiotics indicates that AO-AgNPs can be used as biomedical agents in various areas. Moreover, their suppressive effect on cancerous cell lines showed that they have the potential to be used as an anticancer agent, but due to their proliferative effect on healthy cell lines, care should be taken in determining the appropriate dose.
Keywords: Ag NPs; Anchusa officinalis; antimicrobial activity; biochemical composition; cytotoxic activity; green synthesis.
© 2025 Keskin et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Synthesis, characterization and evaluation of antimicrobial and cytotoxic activities of biogenic silver nanoparticles synthesized from Streptomyces xinghaiensis OF1 strain.World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2018 Jan 5;34(2):23. doi: 10.1007/s11274-017-2406-3. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2018. PMID: 29305718 Free PMC article.
-
Silver Nanoparticles Prepared Using Magnolia officinalis Are an Effective Antimicrobial Agent on Candida albicans, Escherichia coli, and Staphylococcus aureus.Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2025 Apr;17(2):625-639. doi: 10.1007/s12602-023-10179-y. Epub 2023 Oct 16. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2025. PMID: 37843750
-
Antimicrobial and cytotoxic activity of silver nanoparticles synthesized from two haloalkaliphilic actinobacterial strains alone and in combination with antibiotics.J Appl Microbiol. 2018 Jun;124(6):1411-1424. doi: 10.1111/jam.13723. Epub 2018 Mar 23. J Appl Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29427473
-
Unlocking the power of nanohybrids: A critical review on carbon nanomaterial-functionalized silver nanoparticles for advanced antimicrobial applications.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2025 Aug;252:114678. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2025.114678. Epub 2025 Apr 6. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2025. PMID: 40209605 Review.
-
Eco-friendly nanotherapeutics: Metallic nanoparticles for targeting breast cancer.Eur J Pharmacol. 2025 Jun 5;996:177603. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2025.177603. Epub 2025 Apr 4. Eur J Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40189083 Review.
Cited by
-
Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using Plant Extracts: A Comprehensive Review of Physicochemical Properties and Multifunctional Applications.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jun 27;26(13):6222. doi: 10.3390/ijms26136222. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40650001 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Larvicidal efficacy of silk sericin-capped silver nano bioinsecticides (SS-AgNBIs) against Aedes aegypti.Sci Rep. 2025 Aug 4;15(1):28386. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-12959-8. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40759685 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kandav G, Sharma T. Green synthesis: an eco friendly approach for metallic nanoparticles synthesis. Part Sci Technol. 2024;42:874–894. doi:10.1080/02726351.2023.2281452 - DOI
-
- Mughal B, Zaidi SZJ, Zhang X, Hassan SU. Biogenic nanoparticles: synthesis, characterisation and applications. Appl Sci. 2021;11:2598.
-
- Devi L, Kushwaha P, Ansari TM, Kumar A, Rao A. Recent trends in biologically synthesized metal nanoparticles and their biomedical applications: a review. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2023:1–17. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

