Selective expression of Pneumocystis antigens in different patients during a suspected outbreak of Pneumocystis pneumonia
- PMID: 40243367
- PMCID: PMC12077189
- DOI: 10.1128/mbio.00692-25
Selective expression of Pneumocystis antigens in different patients during a suspected outbreak of Pneumocystis pneumonia
Abstract
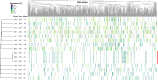
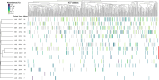
The fungus Pneumocystis jirovecii causes severe pneumonia in immunocompromised individuals. It harbors a system of surface antigenic variation involving six families of major surface glycoproteins (Msg). We determined the repertoires of P. jirovecii msg genes of the most abundant family-I present in 15 Swiss patients with Pneumocystis pneumonia (PCP) enrolled randomly. The highly repetitive msg-I genes were sequenced using generic PCRs followed by circular consensus sequencing with long reads. In contrast to the other 12 patients, three renal transplant recipients (RTRs) harbored the same repertoire of msg-I genes. Multilocus genotyping showed that these RTRs were infected by the same P. jirovecii genotype that differed from those present in the other 12 patients. These observations suggested that these RTRs were involved in an outbreak of PCP due to interhuman transmission or a common source of the fungus. Although they harbored the same repertoire of msg-I genes, the sets of msg-I genes that were expressed differed between the three patients. This suggested that selective expression of P. jirovecii surface antigens might have played a role in the pathogenesis of PCP by allowing escape from the immune response specific to each patient. Although expected for a family of genes, this is the first time that selective expression of antigens is observed in Pneumocystis. The previously described adaptation of P. jirovecii to infect solid organ transplant (SOT) recipients through resistance to the immunosuppressant mycophenolate probably also favored the suspected outbreak. Moreover, our study supports the idea that various P. jirovecii genotypes can adapt to infect SOT recipients.IMPORTANCEThe fungus Pneumocystis causes severe pneumonia in patients with weakened immune systems. It possesses a genetic system to vary the antigens at the surface of its cells that are presented to the immune system of the patient. We report for the first time that this system may have been implicated in the infections of renal transplant recipients involved in a suspected outbreak. Our observations suggest that the antigens presented might be selected to avoid the elimination of the fungus by the immune response specific to each patient. The resistance of the fungus to the immunosuppressant mycophenolate administered to these patients to prevent organ rejection probably also played a role in the infections during the suspected outbreak.
Keywords: PCP; PJP; PacBio circular consensus sequencing; Pneumocystis jirovecii; Pneumocystis pneumonia; cluster; genotyping; major surface glycoprotein.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
