A systematic review and sequential explanatory synthesis: Artificial intelligence in healthcare education, a case of nursing
- PMID: 40243390
- PMCID: PMC12005066
- DOI: 10.1111/inr.70018
A systematic review and sequential explanatory synthesis: Artificial intelligence in healthcare education, a case of nursing
Abstract
Aim: This review aims to explore the impact of artificial intelligence (AI) on knowledge acquisition, skills development, and attitudes among nursing students.
Background: AI offers hopeful opportunities to enhance learning experiences and prepare future healthcare professionals.
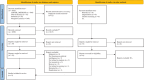
Methods: This was a sequential explanatory mixed-method systematic review. This review was conducted in line with the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines. A comprehensive electronic database was searched to identify relevant studies. Eligibility criteria were studies examining the impacts of AI interventions on nursing students' knowledge, skills, or attitudes. The methodological quality of the studies was assessed using the mixed-method appraisal tool.
Results: Nine research articles were included in the review. These studies utilized both quantitative and qualitative methodologies to examine the impact of AI on nursing students. Quantitative studies found positive relations between AI interventions and knowledge acquisition, skills development, and attitudes toward AI among nursing students. Qualitative findings revealed the positive outcomes of AI in fostering learning engagement, self-efficacy, and confidence.
Conclusions: AI shows potential for supporting knowledge acquisition, skills development, and fostering positive attitudes among nursing students.
Implications for nursing practice and nursing policy: AI-driven interventions enhance nursing education by improving clinical decision-making, confidence, and knowledge acquisition. By integrating AI, nurse educators can develop more interactive, personalized, and impactful learning environments that may help students with the complexities of contemporary healthcare. Policies, standardized guidelines, and faculty development programs may be developed that can promote ethical AI integration, equitable access, and faculty training. These changes can be considered essential to maximize AI's benefits.
Keywords: artificial intelligence; attitude; knowledge acquisition; learning; nursing education; skill development; systematic review.
© 2025 The Author(s). International Nursing Review published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of International Council of Nurses.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflict of interest has been declared by the author(s).
Similar articles
-
Navigating the integration of artificial intelligence in the medical education curriculum: a mixed-methods study exploring the perspectives of medical students and faculty in Pakistan.BMC Med Educ. 2025 Feb 20;25(1):273. doi: 10.1186/s12909-024-06552-2. BMC Med Educ. 2025. PMID: 39979912 Free PMC article.
-
Redefining pedagogy with artificial intelligence: How nursing students are shaping the future of learning.Nurse Educ Pract. 2025 Mar;84:104330. doi: 10.1016/j.nepr.2025.104330. Epub 2025 Mar 13. Nurse Educ Pract. 2025. PMID: 40090205
-
Student and educator experiences of maternal-child simulation-based learning: a systematic review of qualitative evidence protocol.JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2015 Jan;13(1):14-26. doi: 10.11124/jbisrir-2015-1694. JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2015. PMID: 26447004
-
Nursing Student and Faculty Attitudes, Perceptions, and Behavioral Intentions of Artificial Intelligence Use in Nursing Education: An Integrative Review.Nurs Educ Perspect. 2025 Mar-Apr 01;46(2):E7-E11. doi: 10.1097/01.NEP.0000000000001372. Epub 2025 Jan 24. Nurs Educ Perspect. 2025. PMID: 39853199 Review.
-
Nursing students learning transfer from classroom to clinical practice: An integrative review.Nurse Educ Pract. 2023 Aug;71:103731. doi: 10.1016/j.nepr.2023.103731. Epub 2023 Jul 24. Nurse Educ Pract. 2023. PMID: 37517230 Review.
Cited by
-
Integration of artificial intelligence in nursing education: a cross-national exploration.BMC Nurs. 2025 Aug 5;24(1):1026. doi: 10.1186/s12912-025-03689-3. BMC Nurs. 2025. PMID: 40764580 Free PMC article.
References
-
- American Association of Colleges of Nursing (2023) New data show enrollment declines in schools of nursing, raising concerns about the nation's nursing workforce . May 2. [Accessed 17th February 2025]. Available at: https://www.aacnnursing.org/news‐data/all‐news/new‐data‐show‐enrollment‐...
-
- Baashar, Y. , Alkawsi, G. , Mustafa, A. , Alkahtani, A.A. , Alsariera, Y.A. , Ali, A.Q. , Hashim, W. & Tiong, S.K. (2022) Toward predicting student's academic performance using artificial neural networks (ANNs). Applied Sciences, 12 (3), 1289. 10.3390/app12031289 - DOI
-
- Bloom, B.S. & Krathwohl, D.R. (1984) Taxonomy of educational objectives: the classification of educational goals. Michigan: David McKay Company.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources