The Central FacilitaTOR: Coordinating Transcription and Translation in Eukaryotes
- PMID: 40243440
- PMCID: PMC11989106
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26072845
The Central FacilitaTOR: Coordinating Transcription and Translation in Eukaryotes
Abstract
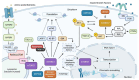
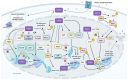
One of the biggest challenges to eukaryotic gene expression is coordinating transcription in the nucleus and protein synthesis in the cytoplasm. However, little is known about how these major steps in gene expression are connected. The Target of Rapamycin (TOR) signaling pathway is crucial in connecting these critical phases of gene expression. Highly conserved among eukaryotic cells, TOR regulates growth, metabolism, and cellular equilibrium in response to changes in nutrients, energy levels, and stress conditions. This review examines the extensive role of TOR in gene expression regulation. We highlight how TOR is involved in phosphorylation, remodeling chromatin structure, and managing the factors that facilitate transcription and translation. Furthermore, the critical functions of TOR extend to processing RNA, assembling RNA-protein complexes, and managing their export from the nucleus, demonstrating its wide-reaching impact throughout the cell. Our discussion emphasizes the integral roles of TOR in bridging the processes of transcription and translation and explores how it orchestrates these complex cellular processes.
Keywords: RNA export; RNA processing; TOR; mRNA turnover; ribosome biogenesis; stress response; transcription; translation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

