Synergistic Anti-Cancer Activity of Melittin and Erlotinib in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
- PMID: 40243485
- PMCID: PMC11989111
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26072903
Synergistic Anti-Cancer Activity of Melittin and Erlotinib in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
Abstract
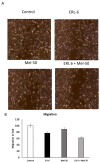
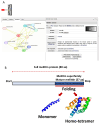
Lung cancer remains a leading cause of cancer-related mortality worldwide. Despite advancements in current therapies, the development of drug resistance and the need for improved treatment outcomes necessitate the exploration of novel therapeutic approaches. This study aimed to investigate the synergistic anti-cancer effects of Melittin, a bee venom peptide, in combination with Erlotinib, an EGFR inhibitor, in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). The study evaluated the combined effects of Melittin and Erlotinib on A549 NSCLC cells. Cell viability, proliferation, migration, and apoptosis were assessed using standard in vitro assays. Mechanistic studies investigated the impact of the combination treatment on key signaling pathways, including those involving JAK2 and JAK3. Molecular docking simulations were performed to predict the binding interactions between Melittin and these kinases. The combination of Melittin and Erlotinib significantly inhibited A549 cell proliferation and migration, with a marked reduction in cell viability and enhanced apoptosis compared to either agent alone. Mechanistically, Melittin demonstrated interactions with JAK2 and JAK3, key proteins involved in apoptotic signaling. Molecular docking simulations further supported these findings, predicting strong binding affinities between Melittin and both kinases. These findings demonstrate a synergistic anti-cancer effect of Melittin and Erlotinib in A549 NSCLC cells. The observed interactions with JAK2 and JAK3 suggest a potential mechanism for Melittin's activity. These results highlight the potential of Melittin as a promising adjuvant to Erlotinib for the treatment of NSCLC.
Keywords: Erlotinib; JAK2/JAK3 signaling; Melittin; lung cancer; synergistic anti-cancer effects.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflicts of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
A Comparative Study of Melittins from Apis florea and Apis mellifera as Cytotoxic Agents Against Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) Cells and Their Combination with Gefitinib.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Mar 11;26(6):2498. doi: 10.3390/ijms26062498. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40141140 Free PMC article.
-
JAK2 inhibitor TG101348 overcomes erlotinib-resistance in non-small cell lung carcinoma cells with mutated EGF receptor.Oncotarget. 2015 Jun 10;6(16):14329-43. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.3685. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 25869210 Free PMC article.
-
Physalin A exerts anti-tumor activity in non-small cell lung cancer cell lines by suppressing JAK/STAT3 signaling.Oncotarget. 2016 Feb 23;7(8):9462-76. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.7051. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 26843613 Free PMC article.
-
Unravelling key signaling pathways for the therapeutic targeting of non-small cell lung cancer.Eur J Pharmacol. 2025 Jul 5;998:177494. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2025.177494. Epub 2025 Mar 14. Eur J Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40090536 Review.
-
Melittin: A promising therapeutic agent for rheumatoid arthritis treatment.Toxicon. 2025 Apr;258:108335. doi: 10.1016/j.toxicon.2025.108335. Epub 2025 Mar 25. Toxicon. 2025. PMID: 40147796 Review.
Cited by
-
2-Amino-3-Chlorobenzoic Acid from Streptomyces coelicolor: A Cancer Antagonist Targeting PI3K/AKT Markers via miRNA Modulation.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025 Apr 24;18(5):620. doi: 10.3390/ph18050620. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40430441 Free PMC article.
References
-
- WHO (World Health Organization) Fact Sheet: Lung Cancer. 2023. [(accessed on 26 October 2024)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/lung-cancer.
-
- Pawar A. Exploring the Therapeutic Promise of Melittin: Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Cancer Applications of Bee Venom. J. Intern. Med. Pharmacol. 2024;1:01–094.
-
- Rehman H.M., Rehman H.M., Ahmed N., IMRAN M. In silico Design and Evaluation of Novel Cell Targeting Melittin-Interleukin-24 Fusion Protein: A Potential Drug Candidate Against Breast Cancer. Sains Malaysiana. 2023;52:3223–3237.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

