Trabectedin Induces Synthetic Lethality via the p53-Dependent Apoptotic Pathway in Ovarian Cancer Cells Without BRCA Mutations When Used in Combination with Niraparib
- PMID: 40243501
- PMCID: PMC11989182
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26072921
Trabectedin Induces Synthetic Lethality via the p53-Dependent Apoptotic Pathway in Ovarian Cancer Cells Without BRCA Mutations When Used in Combination with Niraparib
Abstract
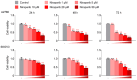
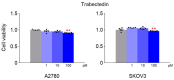
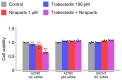
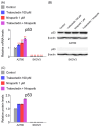
This study investigated whether combining niraparib and trabectedin in BRCA-proficient epithelial ovarian cancer induces deficiencies in ssDNA break repair and dsDNA homologous recombination, leading to synthetic lethality. A2780 and SKOV3 ovarian cancer cell lines were treated with niraparib and trabectedin. Cell viability was assessed using CCK-8 assays, while RT-qPCR and Western blot analyzed the expression of DNA repair and apoptosis-related genes. Apoptosis was evaluated via Annexin V/PI assays. The combination therapy exhibited a synergistic effect on A2780 cells but not on SKOV3 cells. Treatment reduced BRCA1, BRCA2, RAD51, PARP1, and PARP2 expression, indicating impaired DNA repair. γ-H2AX levels increased, suggesting DNA damage. The therapy also upregulated p53, PUMA, NOXA, BAX, BAK, and p21, promoting p53-mediated apoptosis and cell cycle arrest. Apoptosis induction was confirmed via Annexin V/PI assays. Silencing p53 with siRNA abolished all synergistic effects in A2780 cells. Niraparib and trabectedin combination therapy impairs DNA repair in BRCA-proficient ovarian cancer, leading to synthetic lethality through p53-dependent apoptosis.
Keywords: homologous recombination deficiency; ovarian carcinoma; poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitor; synthetic lethality; trabectedin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures





References
-
- DiSilvestro P., Banerjee S., Colombo N., Scambia G., Kim B.G., Oaknin A., Friedlander M., Lisyanskaya A., Floquet A., Leary A., et al. Overall Survival with Maintenance Olaparib at a 7-Year Follow-Up in Patients with Newly Diagnosed Advanced Ovarian Cancer and a BRCA Mutation: The SOLO1/GOG 3004 Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023;41:609–617. doi: 10.1200/JCO.22.01549. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Poveda A., Floquet A., Ledermann J.A., Asher R., Penson R.T., Oza A.M., Korach J., Huzarski T., Pignata S., Friedlander M., et al. Olaparib tablets as maintenance therapy in patients with platinum-sensitive relapsed ovarian cancer and a BRCA1/2 mutation (SOLO2/ENGOT-Ov21): A final analysis of a double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2021;22:620–631. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(21)00073-5. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

