Immune Modulation and Immunotherapy in Solid Tumors: Mechanisms of Resistance and Potential Therapeutic Strategies
- PMID: 40243502
- PMCID: PMC11989189
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26072923
Immune Modulation and Immunotherapy in Solid Tumors: Mechanisms of Resistance and Potential Therapeutic Strategies
Abstract
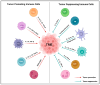
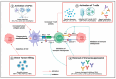
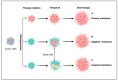
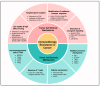
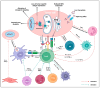
Understanding the modulation of specific immune cells within the tumor microenvironment (TME) offers new hope in cancer treatments, especially in cancer immunotherapies. In recent years, immune modulation and resistance to immunotherapy have become critical challenges in cancer treatments. However, novel strategies for immune modulation have emerged as promising approaches for oncology due to the vital roles of the immunomodulators in regulating tumor progression and metastasis and modulating immunological responses to standard of care in cancer treatments. With the progress in immuno-oncology, a growing number of novel immunomodulators and mechanisms are being uncovered, offering the potential for enhanced clinical immunotherapy in the near future. Thus, gaining a comprehensive understanding of the broader context is essential. Herein, we particularly summarize the paradoxical role of tumor-related immune cells, focusing on how targeted immune cells and their actions are modulated by immunotherapies to overcome immunotherapeutic resistance in tumor cells. We also highlight the molecular mechanisms employed by tumors to evade the long-term effects of immunotherapeutic agents, rendering them ineffective.
Keywords: emerging strategies; immune cells; immune modulation; immunotherapy; therapeutic outcomes; therapeutic resistance; tumor microenvironment.
Conflict of interest statement
Author D.K. was employed by the company NADIANBIO Co., Ltd. and KHAS Health Pvt. Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

