The Spectrum of Small Heat Shock Protein B8 (HSPB8)-Associated Neuromuscular Disorders
- PMID: 40243504
- PMCID: PMC11989117
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26072905
The Spectrum of Small Heat Shock Protein B8 (HSPB8)-Associated Neuromuscular Disorders
Abstract
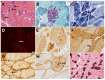
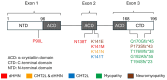
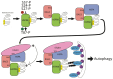
The heat shock protein B8 (HSPB8) is one of the small heat shock proteins (sHSP or HSPB) and is a ubiquitous protein in various organisms, including humans. It is highly expressed in skeletal muscle, heart, and neurons. It plays a crucial role in identifying misfolding proteins and participating in chaperone-assisted selective autophagy (CASA) for the removal of misfolded and damaged, potentially cytotoxic proteins. Mutations in HSPB8 can cause distal hereditary motor neuropathy (dHMN), Charcot-Marie-Tooth (CMT) disease type 2L, or myopathy. The disease can manifest from childhood to mid-adulthood. Most missense mutations in the N-terminal and α-crystallin domains of HSPB8 lead to dHMN or CMT2L. Frameshift mutations in the C-terminal domain (CTD), resulting in elongation of the HSPB8 C-terminal, cause myopathy with myofibrillar pathology and rimmed vacuoles. Myopathy and motor neuropathy can coexist. HSPB8 frameshift mutations in the CTD result in HSPB8 mutant aggregation, which weakens the CASA ability to direct misfolded proteins to autophagic degradation. Cellular and animal models indicate that HSPB8 mutations drive pathogenesis through a toxic gain-of-function mechanism. Currently, no cure is available for HSPB8-associated neuromuscular disorders, but numerous therapeutic strategies are under investigation spanning from small molecules to RNA interference to exogenous HSPB8 delivery.
Keywords: CASA; CMT2L; CTM2; HMN; HSPB8; dHMN; myofibrillar myopathy; myopathy; rimmed vacuoles.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
HSPB8 frameshift mutant aggregates weaken chaperone-assisted selective autophagy in neuromyopathies.Autophagy. 2023 Aug;19(8):2217-2239. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2023.2179780. Epub 2023 Feb 28. Autophagy. 2023. PMID: 36854646 Free PMC article.
-
RNA Interference Targeting Small Heat Shock Protein B8 Failed to Improve Distal Hereditary Motor Neuropathy in the Mouse Model.J Gene Med. 2025 Feb;27(2):e70013. doi: 10.1002/jgm.70013. J Gene Med. 2025. PMID: 39972648
-
Autophagy induction by piplartine ameliorates axonal degeneration caused by mutant HSPB1 and HSPB8 in Charcot-Marie-Tooth type 2 neuropathies.Autophagy. 2025 May;21(5):1116-1143. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2024.2439649. Epub 2024 Dec 27. Autophagy. 2025. PMID: 39698979 Free PMC article.
-
Small heat shock proteins in neurodegenerative diseases.Cell Stress Chaperones. 2020 Jul;25(4):679-699. doi: 10.1007/s12192-020-01101-4. Epub 2020 Apr 22. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2020. PMID: 32323160 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuromuscular Diseases Due to Chaperone Mutations: A Review and Some New Results.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Feb 19;21(4):1409. doi: 10.3390/ijms21041409. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32093037 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Evgrafov O.V., Mersiyanova I., Irobi J., Van Den Bosch L., Dierick I., Leung C.L., Schagina O., Verpoorten N., Van Impe K., Fedotov V., et al. Mutant small heat-shock protein 27 causes axonal Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease and distal hereditary motor neuropathy. Nat. Genet. 2004;36:602–606. doi: 10.1038/ng1354. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

