X-Linked Hypophosphatemia Management in Adults: An International Working Group Clinical Practice Guideline
- PMID: 40243526
- PMCID: PMC12261105
- DOI: 10.1210/clinem/dgaf170
X-Linked Hypophosphatemia Management in Adults: An International Working Group Clinical Practice Guideline
Abstract
Purpose: An international working group (IWG) consisting of experts in X-linked hypophosphatemia (XLH) developed global guidelines providing a comprehensive, evidence-based approach to XLH diagnosis, management, and monitoring.
Methods: The IWG, consisting of 43 members as well as methodologists and a patient partner, conducted 2 systematic reviews (SRs) and narrative reviews to address key areas. The SRs addressed the impact of burosumab compared to conventional therapy (phosphate and active vitamin D) or no therapy on patient-important outcomes in adults. They also evaluated conventional therapy compared to no therapy. GRADE methodology was applied to evaluate the certainty of evidence. Non-GRADED recommendations were made in the presence of insufficient evidence to conduct SRs. These guidelines have been reviewed and endorsed by several medical and patient societies and organizations.
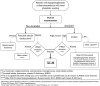
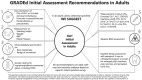
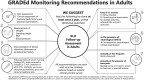
Results: The diagnosis of XLH is based on integrating clinical evaluation, laboratory findings confirming renal phosphate wasting (following exclusion of conditions mimicking XLH), and skeletal imaging. Fibroblast growth factor 23 measurement and DNA analysis are of value in the diagnosis, if available. Pathogenic or likely pathogenic variants in the PHEX gene are confirmatory but not necessary for the diagnosis. Management requires a multidisciplinary team knowledgeable and experienced in XLH. Effective medical therapy with burosumab can improve fracture and pseudofracture healing.
Main conclusion: In adults with XLH and fractures or pseudofractures, burosumab is recommended over no therapy (strong recommendation, GRADEd). Additionally, burosumab is suggested as the preferred treatment compared to conventional therapy (conditional recommendation, GRADEd) in the absence of fractures or pseudofractures. If burosumab is not available, symptomatic adults should be treated with conventional therapy (Non-GRADEd recommendation).
Keywords: X-linked hypophosphatemia (XLH); adult XLH; clinical practice guidelines; consensus.
© The Author(s) 2025. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Endocrine Society.
Figures
References
-
- Liu S, Tang W, Zhou J, et al. Fibroblast growth factor 23 is a counter-regulatory phosphaturic hormone for vitamin D. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2006;17(5):1305‐1315. - PubMed
-
- Che H, Roux C, Etcheto A, et al. Impaired quality of life in adults with X-linked hypophosphatemia and skeletal symptoms. Eur J Endocrinol. 2016;174(3):325‐333. - PubMed
-
- Biosse Duplan M, Coyac BR, Bardet C, et al. Phosphate and vitamin D prevent periodontitis in X-linked hypophosphatemia. J Dent Res. 2017;96(4):388‐395. - PubMed
-
- Insogna KL, Briot K, Imel EA, et al. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial evaluating the efficacy of burosumab, an anti-FGF23 antibody, in adults with X-linked hypophosphatemia: week 24 primary analysis. J Bone Miner Res. 2018;33(8):1383‐1393. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources