Unveiling Genetic Markers for Milk Yield in Xinjiang Donkeys: A Genome-Wide Association Study and Kompetitive Allele-Specific PCR-Based Approach
- PMID: 40243566
- PMCID: PMC11988640
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26072961
Unveiling Genetic Markers for Milk Yield in Xinjiang Donkeys: A Genome-Wide Association Study and Kompetitive Allele-Specific PCR-Based Approach
Abstract
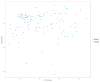
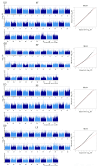
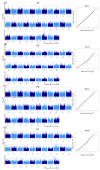
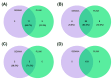
Lactation traits are critical economic attributes in domestic animals. This study investigates genetic markers and functional genes associated with lactation traits in Xinjiang donkeys. We analyzed 112 Xinjiang donkeys using 10× whole genome re-sequencing to obtain genome-wide single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs). Genome-wide association analyses were conducted using PLINK 2.0 and GEMMA 0.98.5 software, employing mixed linear models to assess several lactation traits: average monthly milk yield (AY), fat percentage (FP), protein percentage (PP), and lactose percentage (LP). A total of 236 SNPs were significantly associated with one or more milk production traits (p < 0.000001). While the two-software identified distinct SNP associations, they consistently detected the same 11, 95, 5, and 103 SNPs for AY, FP, PP, and LP, respectively. Several of these SNPs are located within potential candidate genes, including glycosylphosphatidylinositol anchored high density lipoprotein binding protein 1 (GPIHBP1), FLII actin remodeling protein (FLII), mitochondrial topoisomerase 1 (TOP1MT), thirty-eight-negative kinase 1 (TNK1), polo like kinase 1 (PLK1), notch homolog 1 (NOTCH1), developmentally regulated GTP-binding protein 2 (DRG2), mitochondrial elongation factor 2 (MIEF2), glutamine-fructose-6-phosphate transaminase 2 (GFPT2), and dual-specificity tyrosine phosphorylation-regulated kinase 2 (DYRK2). Additionally, we validated the polymorphism of 16 SNPs (10 genes) using Kompetitive Allele Specific PCR, revealing that TOP1MT_g.9133371T > C, GPIHBP1_g.38365122C > T, DRG2_g.4912631C > A, FLII_g.5046888C > T, and PLK1_g.23585377T > C were significantly correlated with average daily milk yield and total milk yield in the studied donkeys. This study represents the first genome-wide association analysis of markers and milk components in Xinjiang donkeys, offering valuable insights into the genetic mechanisms underlying milk production traits. Further research with larger sample sizes is essential to confirm these findings and identify potential causal genetic variants.
Keywords: GWAS; SNPs; Xinjiang donkey; candidate gene; milk.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Study on lactation performance and development of KASP marker for milk traits in Xinjiang donkey (Equus asinus).Anim Biotechnol. 2023 Dec;34(7):2724-2735. doi: 10.1080/10495398.2022.2114002. Epub 2022 Aug 25. Anim Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 36007548
-
A Genome-Wide Association Study of the Chest Circumference Trait in Xinjiang Donkeys Based on Whole-Genome Sequencing Technology.Genes (Basel). 2023 May 14;14(5):1081. doi: 10.3390/genes14051081. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37239441 Free PMC article.
-
Prospecting genomic regions associated with milk production traits in Egyptian buffalo.J Dairy Res. 2020 Nov;87(4):389-396. doi: 10.1017/S0022029920000953. Epub 2020 Nov 13. J Dairy Res. 2020. PMID: 33185171
-
Genetic Effects of LPIN1 Polymorphisms on Milk Production Traits in Dairy Cattle.Genes (Basel). 2019 Apr 2;10(4):265. doi: 10.3390/genes10040265. Genes (Basel). 2019. PMID: 30986988 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring genetic variants affecting milk production traits through genome-wide association study in Vrindavani crossbred cattle of India.Trop Anim Health Prod. 2025 Mar 6;57(2):104. doi: 10.1007/s11250-025-04348-0. Trop Anim Health Prod. 2025. PMID: 40047962
References
-
- Blasi F., Montesano D., De Angelis M., Maurizi A., Ventura F., Cossignani L., Simonetti M., Damiani P. Results of stereospecific analysis of triacylglycerol fraction from donkey, cow, ewe, goat and buffalo milk. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2008;21:1–7. doi: 10.1016/j.jfca.2007.06.005. - DOI
-
- Ma L., Su D.Q., Ji C.F., Ding Y.S., Zhang L., Yu D. Study on health protection efficacy of fresh donkey’s milk. Food Sci. 2008;29:423–426.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

