Adiponectin and TNF-Alpha Differentially Mediate the Association Between Cystatin C and Oxidized LDL in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients
- PMID: 40243674
- PMCID: PMC11988364
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26073001
Adiponectin and TNF-Alpha Differentially Mediate the Association Between Cystatin C and Oxidized LDL in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients
Abstract
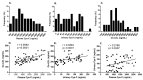
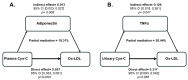
In individuals with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), elevated levels of both plasma and urinary cystatin C (Cys-C) contribute to increased oxidation, which in turn accelerates the oxidation of low-density lipoprotein (LDL). This process may worsen the development of atherosclerosis and cardiovascular disease by promoting endothelial dysfunction and inflammation. Despite its potential significance, the relationship between Cys-C and oxidized LDL (ox-LDL) in T2DM remains poorly understood. This study investigated the relationship between plasma and urinary Cys-C and ox-LDL levels in T2DM patients. The cohort included 57 patients with T2DM (mean age 61.14 ± 9.99 years; HbA1c 8.66 ± 1.60% and BMI 35.15 ± 6.65 kg/m2). Notably, 95% of the patients had hypertension, 82% had dyslipidemia, 59% had an estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) < 60 mL/min/1.73 m2, 14% had coronary artery disease (CAD), and 5% had a history of stroke. Plasma and urinary Cys-C and ox-LDL levels were measured using ELISA. Adipokine and cytokine levels were measured using the multiplex® MAP Human Adipokine Magnetic Bead Panels. Spearman's correlation analysis revealed a significant positive correlation of plasma and urinary Cys-C with ox-LDL (r = 0.569, p = 0.0001 and r = 0.485, p = 0.0001, respectively). Multivariable regression analysis indicated that both plasma and urinary Cys-C were independently associated with ox-LDL, after adjusting for confounding factors (β = 0.057, p = 0.0001 and β = 0.486, p = 0.003, respectively). Stepwise linear regression identified TNFα and adiponectin as the strongest predictors of the relationship between urinary Cys-C and ox-LDL (β = 0.382, p = 0.0001; r2 = 0.64), while adiponectin alone was the best predictor of the plasma Cys-C and ox-LDL association (β = 0.051, p = 0.005; r2 = 0.46). Furthermore, adiponectin partly mediated the relationship between plasma Cys-C and ox-LDL, explaining 18% of the variance in this association. In contrast, TNFα partly mediated the relationship between urinary Cys-C and ox-LDL, accounting for 28% of the variance. This study emphasizes the complex interaction between Cys-C and ox-LDL in T2DM. It highlights the need for additional research involving larger patient cohorts to improve our understanding of the therapeutic potential of plasma and urinary Cys-C in conjunction with ox-LDL for managing complications associated with T2DM.
Keywords: adipokines; atherosclerosis; cystatin C; cytokines; diabetes; dyslipidemia; endothelial dysfunction; inflammation; insulin resistance; obesity; oxidized LDL; vascular complications.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Plasma Atrial Natriuretic Peptide Predicts Oxidized Low-Density Lipoprotein Levels in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients Independent of Circulating Adipokine and Cytokine.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Feb 21;26(5):1859. doi: 10.3390/ijms26051859. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40076485 Free PMC article.
-
Elevated beta2-glycoprotein I-low-density lipoprotein levels are associated with the presence of diabetic microvascular complications.J Diabetes Complications. 2015 Jan-Feb;29(1):59-63. doi: 10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2014.09.010. Epub 2014 Sep 28. J Diabetes Complications. 2015. PMID: 25449980
-
Effects of acarbose versus glibenclamide on glycemic excursion and oxidative stress in type 2 diabetic patients inadequately controlled by metformin: a 24-week, randomized, open-label, parallel-group comparison.Clin Ther. 2011 Dec;33(12):1932-42. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2011.10.014. Epub 2011 Nov 10. Clin Ther. 2011. PMID: 22078152 Clinical Trial.
-
Oxidized HDL is a potent inducer of adipogenesis and causes activation of the Ang-II and 20-HETE systems in human obese females.Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2016 Mar;123:68-77. doi: 10.1016/j.prostaglandins.2016.04.004. Epub 2016 May 11. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2016. PMID: 27179555 Review.
-
Genetic basis of dyslipidemia in disease precipitation of coronary artery disease (CAD) associated type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2015 Oct;31(7):663-71. doi: 10.1002/dmrr.2630. Epub 2015 Mar 5. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2015. PMID: 25470794 Review.
References
-
- Siracusa C., Carabetta N., Morano M.B., Manica M., Strangio A., Sabatino J., Leo I., Castagna A., Cianflone E., Torella D., et al. Understanding Vascular Calcification in Chronic Kidney Disease: Pathogenesis and Therapeutic Implications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024;25:13096. doi: 10.3390/ijms252313096. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

