From DNA Repair to Redox Signaling: The Multifaceted Role of APEX1 (Apurinic/Apyrimidinic Endonuclease 1) in Cardiovascular Health and Disease
- PMID: 40243693
- PMCID: PMC11988304
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26073034
From DNA Repair to Redox Signaling: The Multifaceted Role of APEX1 (Apurinic/Apyrimidinic Endonuclease 1) in Cardiovascular Health and Disease
Abstract
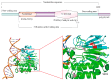
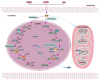
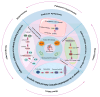
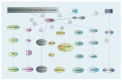
Apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease 1 (APEX1) serves as a potent regulatory factor in innate immunity, exhibiting both redox and endonuclease activities. Its redox function enables the regulation of transcription factors such as NF-κB or STAT3, whereas its endonuclease activity recognizes apurinic/apyrimidinic (AP) sites in damaged DNA lesions during base excision repair (BER) and double-stranded DNA repair, thereby I confirm.anti-inflammatory, antioxidative stress and antiapoptotic effects. APEX1 is expressed in a variety of cell types that constitute the cardiovascular system, including cardiomyocytes, endothelial cells, smooth muscle cells, and immune cells. Emerging genetic and experimental evidence points towards the functional roles of APEX1 in the pathophysiology of cardiovascular diseases, including neointimal formation and atherosclerosis. This review aims to present comprehensive coverage of the up-to-date literature concerning the molecular and cellular functions of APEX1, with a particular focus on how APEX1 contributes to the (dys)functions of different cell types during the pathogenesis of cardiovascular diseases. Furthermore, we underscore the potential of APEX1 as a therapeutic target for the treatment of cardiovascular diseases.
Keywords: APEX1; DNA repair; atherosclerosis; cardiovascular diseases; endonuclease activity; redox activity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Demple B., Linn S. On the recognition and cleavage mechanism of Escherichia coli endodeoxyribonuclease V, a possible DNA repair enzyme. J. Biol. Chem. 1982;257:2848–2855. - PubMed
-
- Linsley W.S., Penhoet E.E., Linn S. Human endonuclease specific for apurinic/apyrimidinic sites in DNA. Partial purification and characterization of mul-tiple forms from placenta. J. Biol. Chem. 1977;252:1235–1242. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

