Analysis of Metabolomic Reprogramming Induced by Infection with Kaposi's Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus Using Untargeted Metabolomic Profiling
- PMID: 40243754
- PMCID: PMC11988554
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26073109
Analysis of Metabolomic Reprogramming Induced by Infection with Kaposi's Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus Using Untargeted Metabolomic Profiling
Abstract
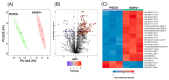
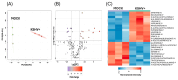
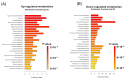
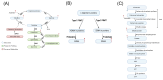
Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV) is an oncogenic double-stranded DNA virus. There are no vaccines or antiviral therapies for KSHV. Identifying the cellular metabolic pathways that KSHV manipulates can broaden the knowledge of how these pathways contribute to sustaining lytic infection, which can be targeted in future therapies to prevent viral spread. In this study, we performed an untargeted metabolomic analysis of KSHV infected telomerase-immortalized gingival keratinocytes (TIGK) cells at 4 h post-infection compared to mock-infected cells. We found that the metabolomic landscape of KSHV-infected TIGK differed from that of the mock. Specifically, a total of 804 differential metabolic features were detected in the two groups, with 741 metabolites that were significantly upregulated, and 63 that were significantly downregulated in KSHV-infected TIGK cells. The differential metabolites included ornithine, arginine, putrescine, dimethylarginine, orotate, glutamate, and glutamine, and were associated with pathways, such as the urea cycle, polyamine synthesis, dimethylarginine synthesis, and de novo pyrimidine synthesis. Overall, our untargeted metabolomics analysis revealed that KSHV infection results in marked rapid alterations in the metabolic profile of the oral epithelial cells. We envision that a subset of these rapid metabolic changes might result in altered cellular functions that can promote viral lytic replication and transmission in the oral cavity.
Keywords: KSHV; de novo infection; metabolomics; oral epithelial cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest relevant to this study.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

