The Role of Puccinia polysora Underw Effector PpEX in Suppressing Plant Defenses and Facilitating Pathogenicity
- PMID: 40243911
- PMCID: PMC11989160
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26073159
The Role of Puccinia polysora Underw Effector PpEX in Suppressing Plant Defenses and Facilitating Pathogenicity
Abstract
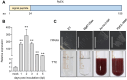
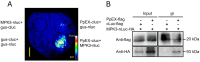
Puccinia polysora Underw, the pathogen that causes southern corn rust (SCR), delivers effectors to manipulate host immune responses. However, the mechanisms by which these effectors modulate host defenses are not well characterized. In this study, we found that the P. polysora effector PpEX is highly upregulated during infection. PpEX suppresses plant immune responses that are initiated by chitin, including the activation of mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs) and the expression of pathogenesis-related (PR) genes. Maize plants transiently expressing PpEX exhibited higher pathogen infection rates, larger colony areas, and greater fungal biomass on their leaves compared to the control group. By employing TurboID proximity labeling technology coupled with mass spectrometry analysis, we discovered potential target proteins of PpEX in maize. The split-luciferase system enabled us to identify ZmMPK3, a component of the MAPK signaling pathway, as an interacting partner of PpEX among the candidate proteins. This interaction was subsequently confirmed by co-immunoprecipitation (Co-IP) experiments. Additionally, we verified that ZmMPK3 plays a positive role in regulating maize resistance to SCR. Thus, PpEX may function as a virulence effector that dampens plant PTI immunity by interacting with ZmMPK3 and impeding the MAPK signaling pathway.
Keywords: PpEX; Puccinia polysora Underw; ZmMPK3; effector; southern corn rust.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Single-cell transcriptomic profiling of maize cell heterogeneity and systemic immune responses against Puccinia polysora Underw.Plant Biotechnol J. 2025 Feb;23(2):549-563. doi: 10.1111/pbi.14519. Epub 2024 Nov 29. Plant Biotechnol J. 2025. PMID: 39612313 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative transcriptome profiling and co-expression network analysis reveals important genes regulating maize response to Southern corn rust.BMC Plant Biol. 2025 Jul 10;25(1):896. doi: 10.1186/s12870-025-06905-z. BMC Plant Biol. 2025. PMID: 40640727 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative proteomics combined with analyses of transgenic plants reveal ZmREM1.3 mediates maize resistance to southern corn rust.Plant Biotechnol J. 2019 Nov;17(11):2153-2168. doi: 10.1111/pbi.13129. Epub 2019 Apr 23. Plant Biotechnol J. 2019. PMID: 30972847 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in Research on Southern Corn Rust, a Devasting Fungal Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Dec 20;25(24):13644. doi: 10.3390/ijms252413644. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39769407 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Harnessing Genetic Resistance in Maize and Integrated Rust Management Strategies to Combat Southern Corn Rust.J Fungi (Basel). 2025 Jan 7;11(1):41. doi: 10.3390/jof11010041. J Fungi (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39852460 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aime M.C. Toward resolving family-level relationships in rust fungi (Uredinales) Mycoscience. 2006;47:112–122. doi: 10.1007/S10267-006-0281-0. - DOI
-
- Sun Q., Li L., Guo F., Zhang K., Dong J., Luo Y., Ma Z. Southern corn rust caused by Puccinia polysora Underw: A review. Phytopathol. Res. 2021;3:25. doi: 10.1186/s42483-021-00102-0. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

