The Analysis of the Glycosyltransferase Activity Gene Family in Gossypium hirsutum and Functional Verification of GTs Conferring Resistance to Verticillium Wilt
- PMID: 40243945
- PMCID: PMC11989804
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26073170
The Analysis of the Glycosyltransferase Activity Gene Family in Gossypium hirsutum and Functional Verification of GTs Conferring Resistance to Verticillium Wilt
Abstract
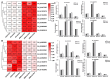
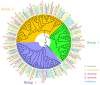
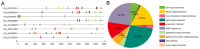
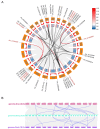
Glycosyltransferases (GTs) play an important role in plant growth and development, as well as responses to biotic and abiotic stresses. However, the function of the GT family in cotton resistance to Verticillium wilt is limited. In the present study, transcriptome analysis revealed eight GTs upregulated in susceptible cotton varieties and downregulated in resistant cotton varieties during early Verticillium dahliae inoculation, indicating they were involved in regulating the infection of V. dahliae in cotton. Promoter analysis revealed a high prevalence of MeJA (methyl jasmonate) and ABA (abscisic acid)-related cis-acting elements among these GTs. Genome-wide and location analysis of the homologous genes showed that these GTs were relatively conserved in evolution. Furthermore, a Virus-Induced Gene Silencing (VIGS) experimental results demonstrated a reduction in disease resistance after GhGT61 silencing. These insights not only deepen our understanding of the GT family's role in cotton, but also provide a foundation for future research on the disease resistance mechanisms of these genes.
Keywords: GhGT61; Glycosyltransferases; Gossypium hirsutum; Verticillium wilt.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Identification and functional analysis of BAG gene family contributing to verticillium wilt resistance in upland cotton.Plant Sci. 2025 Jul;356:112501. doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2025.112501. Epub 2025 Apr 8. Plant Sci. 2025. PMID: 40209939
-
Genome-wide analysis of serine carboxypeptidase-like protein (SCPL) family and functional validation of Gh_SCPL42 unchromosome conferring cotton Verticillium der Verticillium wilt stress in Gossypium hirsutum.BMC Plant Biol. 2022 Sep 1;22(1):421. doi: 10.1186/s12870-022-03804-5. BMC Plant Biol. 2022. PMID: 36045341 Free PMC article.
-
Pan-genome analysis of GT64 gene family and expression response to Verticillium wilt in cotton.BMC Plant Biol. 2024 Sep 30;24(1):893. doi: 10.1186/s12870-024-05584-6. BMC Plant Biol. 2024. PMID: 39343881 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic characteristics and functional analysis provide new insights into long non-coding RNA responsive to Verticillium dahliae infection in Gossypium hirsutum.BMC Plant Biol. 2021 Feb 1;21(1):68. doi: 10.1186/s12870-021-02835-8. BMC Plant Biol. 2021. PMID: 33526028 Free PMC article.
-
Functional characterization of cotton genes responsive to Verticillium dahliae through bioinformatics and reverse genetics strategies.J Exp Bot. 2014 Dec;65(22):6679-92. doi: 10.1093/jxb/eru393. Epub 2014 Oct 17. J Exp Bot. 2014. PMID: 25326626 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

