Ex Vivo Overactivation of Lymphocyte Subsets in Fibrotic Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis Is Blunted by a Sphingosine-1-Phosphate Receptor Ligand
- PMID: 40243992
- PMCID: PMC11989070
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26073197
Ex Vivo Overactivation of Lymphocyte Subsets in Fibrotic Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis Is Blunted by a Sphingosine-1-Phosphate Receptor Ligand
Abstract
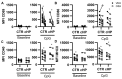
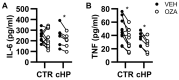
Lymphocytes are central to the pathogenesis of hypersensitivity pneumonitis and a strong body of evidence supports that lymphocytes are modulated by sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor-modifying drugs. This exploratory study aimed to determine if a pharmacological sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor ligand interfered with the activation of lymphocytes obtained from fibrotic hypersensitivity pneumonitis patients. Peripheral blood mononuclear cells of 12 patients and 10 control subjects were submitted to CD3/CD28 stimulation, isolated B cells were incubated with a TLR9 ligand; and we tested how these stimulations were impacted by ozanimod, a sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor ligand. T cell and B cell subsets from patients overexpressed CD69 and cytokines such as TNF and IL-4 in response to CD3/CD28 stimulation, compared to controls. In patients with fibrotic hypersensitivity pneumonitis, ozanimod alleviated CD3/CD28 induction of CD69, IL-4, and TNF in CD8, but not CD4 T cells. In isolated B cells stimulated with a TLR9 ligand, ozanimod reduced cell surface expression of CD69, CD86, and CD40, as well as TNF and IL-6 accumulation in supernatant. We conclude that lymphocyte subsets are functionally impacted in patients with fibrotic hypersensitivity pneumonitis and that ozanimod can interfere ex vivo with the overactivation of B cells and CD8 T cells in response to specific stimuli.
Keywords: BAFF; CD69; S1P; S1P1; S1P5; TLR9; TNF; cytokine; extrinsic allergic alveolitis; ozanimod.
Conflict of interest statement
D.M. received research funding (no honorariums) from Bristol Myers Squibb to perform a clinical trial on the impact of ozanimod in COVID-19 patients from 2020 to 2023.
Figures
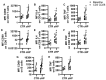

References
-
- Huppe C.A., Blais-Lecours P., Bernatchez E., Lauzon-Joset J.F., Duchaine C., Rosen H., Dion G., McNagny K.M., Blanchet M.R., Morissette M.C., et al. S1P1 Contributes to Endotoxin-enhanced B Cell Functions Involved in Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2020;63:209–218. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2019-0339OC. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bueno M., Zank D., Buendia-Roldan I., Fiedler K., Mays B.G., Alvarez D., Sembrat J., Kimball B., Bullock J.K., Martin J.L., et al. PINK1 attenuates mtDNA release in alveolar epithelial cells and TLR9 mediated profibrotic responses. PLoS ONE. 2019;14:e0218003. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0218003. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Fernandez Perez E.R., Kong A.M., Raimundo K., Koelsch T.L., Kulkarni R., Cole A.L. Epidemiology of Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis among an Insured Population in the United States: A Claims-based Cohort Analysis. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2018;15:460–469. doi: 10.1513/AnnalsATS.201704-288OC. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

