Lidocaine Modulates Cytokine Production and Reprograms the Tumor Immune Microenvironment to Enhance Anti-Tumor Immune Responses in Gastric Cancer
- PMID: 40244064
- PMCID: PMC11989700
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26073236
Lidocaine Modulates Cytokine Production and Reprograms the Tumor Immune Microenvironment to Enhance Anti-Tumor Immune Responses in Gastric Cancer
Abstract
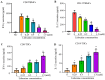
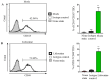
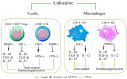
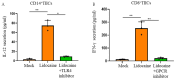
Lidocaine, a local anesthetic, has been shown to modulate immune responses. This study examines its effects on cytokine production in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) from healthy donors and tumor-infiltrating immune cells (TIICs) from gastric cancer patients. PBMCs from healthy donors and TIICs from gastric cancer patients were treated with lidocaine. Cytokine production was assessed using flow cytometry and cytokine assays, with a focus on IFN-γ, IL-12, IL-10, TGF-β, and IL-35 levels. Cytotoxicity against primary gastric cancer cells (PGCCs) was also evaluated. Lidocaine inhibited IFN-γ production in CD8+ PBMCs and IL-12 in CD14+ PBMCs while increasing anti-inflammatory cytokines (IL-10, TGF-β, IL-35) in CD4+CD25+ and CD14+ cells. In TIICs, lidocaine enhanced IFN-γ and IL-12 production in CD8+ and CD14+ cells while reducing IL-10, TGF-β, and IL-35 levels, promoting an M1-like phenotype in macrophages. Mechanistically, lidocaine enhanced IFN-γ production in sorted CD8+ TIICs through G-protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) signaling and increased IL-12 production in sorted CD14+ TIICs via the toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) signaling pathway. Lidocaine also increased IFN-γ production and cytotoxicity in CD8+ TIICs via NF-κB activation. Importantly, lidocaine did not affect the viability of PBMCs, TIICs, or PGCCs at concentrations up to 1.5 mM. Lidocaine reprogrammed the tumor immune microenvironment, enhancing anti-tumor immune responses, suggesting its potential to modulate immune functions in gastric cancer.
Keywords: IFN-γ production; M1 macrophages; NF-κB activation; cytokine modulation; gastric cancer; gastrointestinal disease; immune response; inflammation; lidocaine; tumor-infiltrating immune cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Loftus J.P., Williams J.M., Belknap J.K., Black S.J. In Vivo Priming and Ex Vivo Activation of Equine Neutrophils in Black Walnut Extract-induced Equine Laminitis is Not Attenuated by Systemic Lidocaine Administration. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2010;138:60–69. - PubMed
-
- Renzi P.M., Ginns L.C. Effect of Lidocaine on Natural Killer Activity: Rapid Inhibition of Lysis. Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol. 1990;12:417–437. - PubMed
-
- Elizagaray M.L., Mazitelli I., Pontoriero A., Baumeister E., Docena G., Raimondi C., Correger E., Rumbo M. Lidocaine Reinforces the Anti-inflammatory Action of Dexamethasone on Myeloid and Epithelial Cells Activated by Inflammatory Cytokines or SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Biomed. J. 2023;46:81–92. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Feng G., Liu S., Wang G.L., Liu G.J. Lidocaine Attenuates Lipopolysaccharide-induced Acute Lung Injury Through Inhibiting NF-kappaB Activation. Pharmacology. 2008;81:32–40. - PubMed
-
- Sun H., Sun Y. Lidocaine Inhibits Proliferation and Metastasis of Lung Cancer Cell via Regulation of MiR-539/EGFR Axis. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2019;47:2866–2874. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R111-03/Ditmanson Medical Foundation of Chia-Yi Christian Hospital
- 110S0023A, 111S0023A, 112S0023A, 113S0023A and 114S0023A/iEGG and Animal Biotechnology Center from The Feature Areas Research Center Program within the framework of the Higher Education Sprout Project by the Ministry of Education (MOE) in Taiwan
- TCVGH-NCHU 1127605 , TCVGH-NCHU-1137607 and TCVGH-NCHU-114-OA017/Taichung Veterans General Hospital
- 112-2313-B-005-050-MY3/Ministry of Science and Technology of Taiwan
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

