Protective Effect of Field Horsetail Polyphenolic Extract on Erythrocytes and Their Membranes
- PMID: 40244071
- PMCID: PMC11989917
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26073213
Protective Effect of Field Horsetail Polyphenolic Extract on Erythrocytes and Their Membranes
Abstract
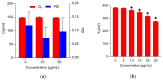
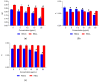
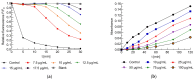
Field horsetail (Equisetum arvense L.) is widely utilized in traditional medicine and is a rich source of bioactive compounds such as flavonoids, phenolic acids, and silica. This study investigates the protective effect of the polyphenolic extract from field horsetail (HLE) on erythrocytes and their cell membranes. The content of polyphenolic compounds in the extract was determined using the HPLC-DAD and Folin-Ciocalteu methods. The extract's hemolytic activity, toxicity, antioxidant activity, and its impact on the physical properties of erythrocytes and lipid membrane were investigated. The antioxidant properties were evaluated using erythrocytes and isolated erythrocyte membranes oxidized by UVC radiation and AAPH. The impact of the extract on the ordering and fluidity of erythrocyte and model lipid membranes was studied. Furthermore, the transmembrane potential, shape of erythrocytes and the dipole potential of the lipid membranes under the influence of HLE were evaluated. The results indicated that HLE extract exhibited no toxicity to erythrocytes and HMEC-1 cells. HLE components effectively protect erythrocytes and their membranes against oxidation. They interact with the outer, polar surface of the erythrocyte membrane and reduce both erythrocyte membrane potential and lipid membrane dipole potential. The HLE polyphenols decrease the concentration of free radicals at the surface of the membrane, where they are located, and serve as a protective barrier, preventing penetration into the membrane.
Keywords: HMEC-1; antioxidant activity; cytotoxicity; dipole potential; fluidity; horsetail; plant extracts; transmembrane potential.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Biophysical mechanism of the protective effect of blue honeysuckle (Lonicera caerulea L. var. kamtschatica Sevast.) polyphenols extracts against lipid peroxidation of erythrocyte and lipid membranes.J Membr Biol. 2014 Jul;247(7):611-25. doi: 10.1007/s00232-014-9677-5. Epub 2014 May 27. J Membr Biol. 2014. PMID: 24862869 Free PMC article.
-
Modification of the properties of biological membrane and its protection against oxidation by Actinidia arguta leaf extract.Chem Biol Interact. 2014 Oct 5;222:50-9. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2014.08.012. Epub 2014 Sep 6. Chem Biol Interact. 2014. PMID: 25199699
-
Protective Effect of Polyphenolic Extracts from Hippophae rhamnoides L. and Reynoutria japonica Houtt. on Erythrocyte Membrane.Molecules. 2024 Jun 28;29(13):3090. doi: 10.3390/molecules29133090. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38999046 Free PMC article.
-
POLYPHENOL CONTENT AND BIOACTIVITY OF SASKATOON (AMELANCHIER ALNIFOLIA NUTT.) LEAVES AND BERRIES.Acta Pol Pharm. 2017 Mar;74(2):660-669. Acta Pol Pharm. 2017. PMID: 29624272
-
Horsetail.2022 Jul 25. LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases; 2012–. 2022 Jul 25. LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases; 2012–. PMID: 35998247 Free Books & Documents. Review.
Cited by
-
Foliar Application of Protein Hydrolysate-Based Biostimulant and Herbal Extracts with Antifungal Properties in Winter Wheat Cultivation as a Strategy to Enhance Cereal Yield.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 May 26;26(11):5089. doi: 10.3390/ijms26115089. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40507900 Free PMC article.
-
Investigation of In Vitro and In Silico Anti-Inflammatory Potential of Carthamus caeruleus L. Root Juice.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jun 21;26(13):5965. doi: 10.3390/ijms26135965. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40649743 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Omotayo O., Maduka C.P., Muonde M., Olorunsogo T.O., Ogugua J.O. The rise of non-communicable diseases: A global health review of challenges and prevention strategies. Int. Med. Sci. Res. J. 2024;4:74–88. doi: 10.51594/imsrj.v4i1.738. - DOI
-
- Cyboran-Mikołajczyk S., Solarska-Ściuk K., Mieszała K., Glatzel-Plucińska N., Matczak K., Kleszczyńska H. The Impact of O-Glycosylation on Cyanidin Interaction with RBCs and HMEC-1 Cells—Structure–Activity Relationships. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019;20:1928. doi: 10.3390/ijms20081928. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

