Genetic and Epigenetic Adaptation Mechanisms of Sheep Under Multi-Environmental Stress Environment
- PMID: 40244095
- PMCID: PMC11989891
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26073261
Genetic and Epigenetic Adaptation Mechanisms of Sheep Under Multi-Environmental Stress Environment
Abstract
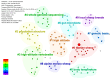
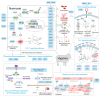
Sheep (Ovis aries), domesticated from wild Asian mouflon ~10,000 years ago, are an important livestock species adapted to various ecological environments. Recent advancements in high-throughput sequencing and global environmental databases have facilitated the exploration of genetic-environmental associations, uncovering the genetic and epigenetic mechanisms behind sheep's adaptation to multiple environments. Studies show that HIF-1α and EPAS1 enhance high-altitude adaptation via hypoxic stress regulation; UCP1 contributes to cold adaptation through non-shivering thermogenesis; SLC4A4 and GPX3 increase drought resistance by regulating renal water reabsorption; and SOCS2 likely plays a role in metabolic and stress response regulation. Additionally, sheep adapt to temperature, drought, and environmental stress through DNA methylation, transcriptional regulation (e.g., SOD1, GPX4), heat shock proteins (e.g., HSP70), and metabolic pathways (e.g., UCP1). These findings offer valuable insights for improving sheep breeding and genetic enhancement. This review summarizes the mechanisms of adaptation to high altitude, cold, heat, drought, and comprehensive climate stress.
Keywords: cold adaptation; drought adaptation; environmental adaptation; genetic mechanisms; high-altitude adaptation; omics; sheep.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The epigenetic mechanisms of adaption to the hot and humid climate in Hu sheep (Ovis aries).Physiol Rep. 2024 Dec;12(24):e16164. doi: 10.14814/phy2.16164. Physiol Rep. 2024. PMID: 39725653 Free PMC article.
-
Whole-Genome Sequencing of Native Sheep Provides Insights into Rapid Adaptations to Extreme Environments.Mol Biol Evol. 2016 Oct;33(10):2576-92. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msw129. Epub 2016 Jul 8. Mol Biol Evol. 2016. PMID: 27401233 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic Insights into Tibetan Sheep Adaptation to Different Altitude Environments.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Nov 19;25(22):12394. doi: 10.3390/ijms252212394. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39596459 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of water stress to plant epigenetic mechanisms in stress and adaptation.Physiol Plant. 2025 Jan-Feb;177(1):e70058. doi: 10.1111/ppl.70058. Physiol Plant. 2025. PMID: 39831338 Review.
-
High-altitude adaptation: Role of genetic and epigenetic factors.J Biosci. 2021;46:107. J Biosci. 2021. PMID: 34840149 Review.
Cited by
-
AMPK Signaling Axis-Mediated Regulation of Lipid Metabolism: Ameliorative Effects of Sodium Octanoate on Intestinal Dysfunction in Hu Sheep.Biomolecules. 2025 May 12;15(5):707. doi: 10.3390/biom15050707. Biomolecules. 2025. PMID: 40427600 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- 32160771/the National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 32302707/the National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 202202AE090005/Major Science and Technology Projects in Yunnan Province
- XDYC-CYCX2022-0029/the "Xingdian Talent" Industry Innovation Talent Program in Yunnan Province
- 2022YFD1100408/the National Key Research and Development Program of China
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

