PD-L1-Targeting Nanoparticles for the Treatment of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: A Preclinical Model
- PMID: 40244130
- PMCID: PMC11989481
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26073295
PD-L1-Targeting Nanoparticles for the Treatment of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: A Preclinical Model
Abstract
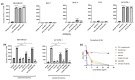
Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) is a highly aggressive form of breast cancer. Common treatments following surgical resection include PD-1-targeting checkpoint inhibitors (pembrolizumab), as 20% of tumors are PD-L1 positive with or without systemic chemotherapy. Over the last several years, our laboratory has developed nano-immune conjugates (NIC) in which hydrophobic chemotherapy drugs like paclitaxel (PTX) and SN38, the active metabolite of irinotecan, are made water soluble by formulating them into albumin-based nanoparticles (nab) that are hydrophobically linked to various IgG1 monoclonal antibodies, creating an antigen-targetable nano-immune conjugate. To date, we have successfully tested PTX containing NICs linked to either VEGF- or CD20-targeted antibodies in two phase I clinical trials against multiple relapsed ovarian/uterine cancer or non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, respectively. Herein, we describe a novel NIC created with either PTX or SN38 that is coated with anti-PD-L1-targeting antibodies for the treatment of a preclinical model of TNBC. In vitro testing suggests that the chemotherapy drug and antibody retain their toxicity and ligand binding capability in the context of the NIC. Furthermore, both the PTX and SN-38 NIC demonstrate superior anti-tumor efficacy relative to antibody and chemotherapy drugs alone in a PD-L1 + MDA-MB-231 human TNBC xenograft model, which could translate clinically to patients with TNBC.
Keywords: mouse xenograft model; nano-immune conjugate (NIC); programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1); triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC).
Conflict of interest statement
S.N.M., W.K.N., and L.G. hold patents on this technology that has been licensed to Sorrento Therapeutics, Inc. Sorrento Therapeutics, Inc. had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures


References
-
- Baranova A., Krasnoselskyi M., Starikov V., Kartashov S., Zhulkevych I., Vlasenko V., Oleshko K., Bilodid O., Sadchikova M., Vinnyk Y. Triple-negative breast cancer: Current treatment strategies and factors of negative prognosis. J. Med. Life. 2022;15:153–161. doi: 10.25122/jml-2021-0108. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Senkus E., Kyriakides S., Ohno S., Penault-Llorca F., Poortmans P., Rutgers E., Zackrisson S., Cardoso F., Committee E.G. Primary breast cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2015;26((Suppl. S5)):v8–v30. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdv298. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

