The Ancestral KEAP1-NRF Pathway in Amphioxus Branchiostoma japonicum: Implications for the Evolution of Antioxidant Defense System
- PMID: 40244297
- PMCID: PMC11989980
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26073427
The Ancestral KEAP1-NRF Pathway in Amphioxus Branchiostoma japonicum: Implications for the Evolution of Antioxidant Defense System
Abstract
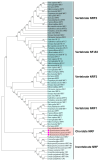
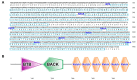
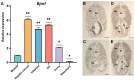
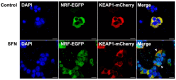
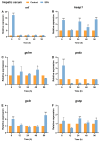
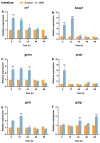
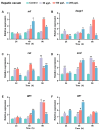
The Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1 (KEAP1)/Nuclear factor E2-related factor 2 (NRF2) pathway is a key mechanism that responds to oxidative stress and xenobiotic stimuli in vertebrates. However, knowledge of its evolutionary origins remains limited. In this study, we identify the ancestral homologues of KEAP1 and NRF (BjKEAP1 and BjNRF) in cephalochordate amphioxus (Branchiostoma japonicum). BjNRF uniquely combines the feature domains of vertebrates NRF1 and NRF2, marking it as an evolutionary intermediate. High expression levels of Bjkeap1 and Bjnrf in the gill, hepatic cecum, and intestine highlight their roles in environmental defense at key interface tissues. Functional studies reveal that BjKEAP1 regulates the cytoplasmic localization of BjNRF. Typical NRF2 activator sulforaphane (SFN) induces its nuclear translocation and significantly elevates the transcriptional expression of BjNRF and phase II detoxification enzymes. Moreover, exposure to the environmental toxin Benzo[a]pyrene (BaP) activates this stress response system. These findings bridge critical gaps in our understanding of this pathway in basal chordates and offer new insights into the evolutionary trajectory of the KEAP1-NRF system. Furthermore, this study highlights crucial implications for the conservation of amphioxus in deteriorating marine environments.
Keywords: KEAP1; NRF1; NRF2; amphioxus; oxidative stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures









Similar articles
-
The molecular mechanism of Nrf2-Keap1 signaling pathway in the antioxidant defense response induced by BaP in the scallop Chlamys farreri.Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019 Sep;92:489-499. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2019.06.006. Epub 2019 Jun 18. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31220575
-
NF-κB and Keap1 Interaction Represses Nrf2-Mediated Antioxidant Response in Rabbit Hemorrhagic Disease Virus Infection.J Virol. 2020 May 4;94(10):e00016-20. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00016-20. Print 2020 May 4. J Virol. 2020. PMID: 32161178 Free PMC article.
-
Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1 (KEAP1) differentially regulates nuclear factor erythroid-2-related factors 1 and 2 (NRF1 and NRF2).J Biol Chem. 2018 Feb 9;293(6):2029-2040. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA117.000428. Epub 2017 Dec 18. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 29255090 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Basis of the KEAP1-NRF2 Signaling Pathway.Mol Cells. 2023 Mar 31;46(3):133-141. doi: 10.14348/molcells.2023.0028. Epub 2023 Mar 27. Mol Cells. 2023. PMID: 36994473 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of oxidative stress in pathophysiology of rheumatoid arthritis: insights into NRF2-KEAP1 signalling.Autoimmunity. 2021 Nov;54(7):385-397. doi: 10.1080/08916934.2021.1963959. Epub 2021 Aug 20. Autoimmunity. 2021. PMID: 34415206 Review.
References
-
- Higgins L.G., Kelleher M.O., Eggleston I.M., Itoh K., Yamamoto M., Hayes J.D. Transcription factor Nrf2 mediates an adaptive response to sulforaphane that protects fibroblasts in vitro against the cytotoxic effects of electrophiles, peroxides and redox-cycling agents. Toxicol. Appl. Pharm. 2009;237:267–280. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2009.03.005. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Moi P., Chan K., Asunis I., Cao A., Kan Y.W. Isolation of NF-E2-related factor 2 (Nrf2), a NF-E2-like basic leucine zipper transcriptional activator that binds to the tandem NF-E2/AP1 repeat of the beta-globin locus control region. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 1994;91:9926–9930. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.21.9926. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

