Recent Advances in Genome Editing and Bioinformatics: Addressing Challenges in Genome Editing Implementation and Genome Sequencing
- PMID: 40244417
- PMCID: PMC11989416
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26073442
Recent Advances in Genome Editing and Bioinformatics: Addressing Challenges in Genome Editing Implementation and Genome Sequencing
Abstract
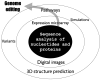
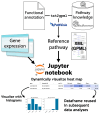
Genome-editing technology has advanced significantly since the 2020 Nobel Prize in Chemistry was awarded for the development of clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats (CRISPR) and CRISPR-associated protein 9 (Cas9). While CRISPR-Cas9 has become widely used in academic research, its social implementation has lagged due to unresolved patent disputes and slower progress in gene function analysis. To address this, new approaches bypassing direct gene function analysis are needed, with bioinformatics and next-generation sequencing (NGS) playing crucial roles. NGS is essential for sequencing the genome of target species, but challenges such as data quality, genome heterogeneity, ploidy, and small individual sizes persist. Despite these issues, advancements in sequencing technologies, like PacBio high-fidelity (HiFi) long reads and high-throughput chromosome conformation capture (Hi-C), have improved genome sequencing. Bioinformatics contributes to genome editing through off-target prediction and target gene selection, both of which require accurate genome sequence information. In this review, I will give updates on the development of genome editing and bioinformatics technologies with a focus on the rapid progress in genome sequencing.
Keywords: bibliome; bioinformatics; database; genome editing; genome sequencing; meta-analysis; next-generation sequencers; pathway; transcriptome.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study.
Figures



Similar articles
-
BATCH-GE: Analysis of NGS Data for Genome Editing Assessment.Methods Mol Biol. 2018;1865:83-90. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-8784-9_6. Methods Mol Biol. 2018. PMID: 30151760
-
Gene Therapy with CRISPR/Cas9 Coming to Age for HIV Cure.AIDS Rev. 2017 Oct-Dec;19(3):167-172. AIDS Rev. 2017. PMID: 29019352
-
Amplification-free long-read sequencing reveals unforeseen CRISPR-Cas9 off-target activity.Genome Biol. 2020 Dec 1;21(1):290. doi: 10.1186/s13059-020-02206-w. Genome Biol. 2020. PMID: 33261648 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in detecting and reducing off-target effects generated by CRISPR-mediated genome editing.J Genet Genomics. 2019 Nov 20;46(11):513-521. doi: 10.1016/j.jgg.2019.11.002. Epub 2019 Nov 22. J Genet Genomics. 2019. PMID: 31911131 Review.
-
Recent advances in CRISPR/Cas9 mediated genome editing in Bacillus subtilis.World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2018 Sep 29;34(10):153. doi: 10.1007/s11274-018-2537-1. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2018. PMID: 30269229 Review.
References
-
- McAuley G.E., Yiu G., Chang P.C., Newby G.A., Campo-Fernandez B., Fitz-Gibbon S.T., Wu X., Kang S.-H.L., Garibay A., Butler J., et al. Human T Cell Generation Is Restored in CD3δ Severe Combined Immunodeficiency through Adenine Base Editing. Cell. 2023;186:1398–1416.e23. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2023.02.027. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

