Unraveling the oncogenic role of LINC00504 and its interaction with miR-545-3p and ARIHI in hepatocellular carcinoma: novel insights for molecular therapy
- PMID: 40244538
- PMCID: PMC12006597
- DOI: 10.1007/s12672-025-02328-2
Unraveling the oncogenic role of LINC00504 and its interaction with miR-545-3p and ARIHI in hepatocellular carcinoma: novel insights for molecular therapy
Abstract
Objectives: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a serious global health threat associated with high morbidity and mortality. The importance of long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) in tumor progression is growing. The aim of this study was to explore the expression, functional properties and molecular mechanisms of LINC00504 in HCC.
Materials and methods: Tumor tissue samples from HCC patients were collected to analyze the expression of LINC00504, miR-545-3p, and ARIH1 mRNA using RT-qPCR, and compared with various HCC cell lines (PLC/PRF/5, SNU-182, Hep3B, HuH-7) and a human normal liver epithelial cell line (THLE-2). Cell proliferation, apoptosis, and invasion were assessed using transfection vectors, CCK8 assay, flow cytometry, and Transwell. Interactions among LINC00504, miR-545-3p, and ARIH1 were confirmed through database predictions and luciferase reporter gene assays.
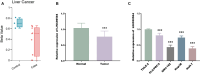
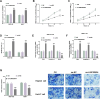
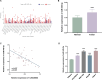
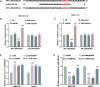
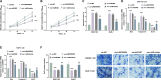
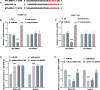
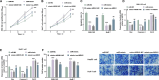
Results: LINC00504 was underexpressed in HCC tissues and cell lines. Upregulation of LINC00504 inhibited cell proliferation, induced apoptosis, increased Bax and Caspase-3, decreased Bcl-2 mRNA, and suppressed invasion. miR-545-3p was overexpressed in HCC cells and was negatively regulated by LINC00504. Overexpression of miR-545-3p counteracted the effects of LINC00504 upregulation. ARIH1 was underexpressed in HCC tissues and had a negative correlation with miR-545-3p. miR-545-3p negatively regulated ARIH1 expression, and ARIH1 overexpression overturned the promotional effects of miR-545-3p on HCC cells.
Conclusion: This study uncovers the significant tumor-suppressing role of LINC00504 in HCC, potentially through a mechanism involving the targeting of miR-545-3p, which in turn inhibits the ARIH1. These findings offer new potential targets for HCC molecular treatment.
Keywords: ARIH1; Cellular processes; HCC; LINC00504; MiR-545-3p.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: The study was performed in line with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki. All protocols of this investigation were approved by the Ethics Committee of Huangshi Central Hospital. The participants'right to be informed about the study was ensured and written informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
