Increasing the health span: unique role for exercise
- PMID: 40244910
- PMCID: PMC12182867
- DOI: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00049.2025
Increasing the health span: unique role for exercise
Abstract
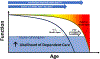
Health span, that period between birth and onset of major disease(s), when adequate physical and cognitive function permit those daily living activities essential to life quality, is lower in the United States than other developed countries. Physical inactivity and excessive calorie intake occupy dominant roles both in the problem, and by redressing them, in the solution. Consequently, this review focuses on evidence that appropriate exercise engagement and calorie restriction (CR) can improve physical and mental health with a view to extending the health span. Humanity, writ large, has grasped these underlying concepts for Millennia but has been largely intransigent to them. Thus, the final section proposes a novel Monty Python-esque approach that encompasses humanity's inimical sense of humor to increase physical fitness and mental health, restore energy balance, sustain better cognitive function, and extend the health span.
Keywords: V̇o2max; calorie restriction; cardiorespiratory fitness; cognitive function; physical activity.
Figures






References
-
- Butler RN. Public interest report no. 23: Exercise, the neglected therapy. J Aging Develop. 8: 193–195, 1977. - PubMed
-
- Booth FW, Hawley JA. The erosion of physical activity in Western societies: an economic death march. Diabetologia. 58: 1730–1734, 2015. - PubMed
-
- Olshansky SJ. From Lifespan to Healthspan. JAMA. 320: 1323–1324, 2018. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- U01 AG020487/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R15 HL137156/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R15 AG078060/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG075556/HHS | National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- R01 AG071717/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL091006/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- Sustained Momentum for Investigators with Laboratories Established
- AG-078060/HHS | National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- R01 AG075556/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- Elizabeth Chapin Burke Chair of Health and Human Sciences
- HL-091006/HHS | National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- AG-020487/HHS | National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- P20GM113109/HHS | National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- U24 AG047121/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R33 AG070455/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- KSU | Johnson Cancer Research Center, Kansas State University (JCRC)
- P20 GM113109/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

