Mycobacterium susceptibility to ivermectin by inhibition of eccD3, an ESX-3 secretion system component
- PMID: 40245093
- PMCID: PMC12005495
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1012936
Mycobacterium susceptibility to ivermectin by inhibition of eccD3, an ESX-3 secretion system component
Abstract
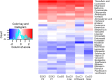
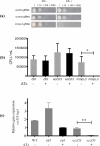
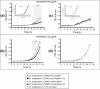
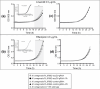
Drug-resistant tuberculosis is a pressing global health issue that requires the development of new drugs or the identification of new therapeutic targets. The ESX-3 secretion system is essential for the Mycobacterium tuberculosis growth and plays a role in iron/zinc homeostasis and virulence. The aim of this study was to evaluate the quaternary interface of EccD3, a component of the ESX-3 secretion system, and to evaluate the association of an eccD3 mutant with drug resistance. The molecular structures of EccD3 protein and other ESX-3 secretion system proteins of the M. tuberculosis were predicted based in homology with the Mycolicibacterium smegmatis tertiary protein structures. According to the in silico results, selamectin, avermectin, ivermectin, and moxidectin were selected as prospective drugs. Selamectin and moxidectin had favorable ΔG values for the EccB3 and EccD3 dimer interfaces, whereas the ESX-3 Protomer 1 interface had the best ΔG + with avermectin, ivermectin, and moxidectin. Furthermore, ivermectin susceptibility increased when the eccD3 gene was inhibited using CRISPRi in M. smegmatis. Blockage of EccD3 increased the ivermectin action, but the modest changes observed may be explained by the compensatory mechanisms or other ivermectin targets in absence of this Esx3 component. Further in vitro and preclinical studies are required to validate our findings.
Copyright: © 2025 Granados-Tristán et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Essential role of the ESX-3 associated eccD3 locus in maintaining the cell wall integrity of Mycobacterium smegmatis.Int J Med Microbiol. 2018 Oct;308(7):784-795. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmm.2018.06.010. Epub 2018 Jun 28. Int J Med Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 30257807
-
ESX-3 secretion system in Mycobacterium: An overview.Biochimie. 2024 Jan;216:46-55. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2023.10.013. Epub 2023 Oct 23. Biochimie. 2024. PMID: 37879428 Review.
-
The Veterinary Anti-Parasitic Selamectin Is a Novel Inhibitor of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis DprE1 Enzyme.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jan 11;23(2):771. doi: 10.3390/ijms23020771. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35054958 Free PMC article.
-
Deep mutational scanning of EccD3 reveals the molecular basis of its essentiality in the mycobacterium ESX secretion system.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Aug 24:2024.08.23.609456. doi: 10.1101/2024.08.23.609456. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 39229178 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Targeting type VII/ESX secretion systems for development of novel antimycobacterial drugs.Curr Pharm Des. 2014;20(27):4346-56. doi: 10.2174/1381612819666131118170717. Curr Pharm Des. 2014. PMID: 24245757 Review.
References
-
- WHO. Global tuberculosis report. 2023.
-
- Peñuelas-Urquides K, González-Escalante L, Villarreal-Treviño L, Silva-Ramírez B, Gutiérrez-Fuentes DJ, Mojica-Espinosa R, et al.. Comparison of gene expression profiles between pansensitive and multidrug-resistant strains of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Curr Microbiol. 2013;67(3):362–71. doi: 10.1007/s00284-013-0376-8 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Arriaga-Guerrero AL, Hernández-Luna CE, Rigal-Leal J, Robles-González RJ, González-Escalante LA, Silva-Ramírez B, et al.. LipF increases rifampicin and streptomycin sensitivity in a Mycobacterium tuberculosis surrogate. BMC Microbiol. 2020;20(1):132. doi: 10.1186/s12866-020-01802-x - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

