Impact of Islet Transplantation on Diabetes Complications and Mortality in Patients Living With Type 1 Diabetes
- PMID: 40245107
- PMCID: PMC12094206
- DOI: 10.2337/dc25-0059
Impact of Islet Transplantation on Diabetes Complications and Mortality in Patients Living With Type 1 Diabetes
Abstract
Objective: This study aimed to evaluate the impact of islet transplantation (IT) on diabetes complications, death, and cancer incidence.
Research design and methods: This retrospective, multicenter, cohort study included patients from three IT clinical trials (intervention group) and from the French health insurance claims database Système National des Données de Santé (SNDS) (control group). Two cohorts of IT recipients were analyzed: IT recipients after kidney transplantation (IAK) and IT recipients alone (ITA). They were matched with patients living with type 1 diabetes (T1D) from the SNDS using a propensity score. The primary outcome was a composite criterion including death, dialysis, amputation, nonfatal stroke, nonfatal myocardial infarction, and transient ischemic attack. The secondary outcome was cancer. Hazard ratio (HRs) and P values were obtained using Cox proportional hazards analysis and log-rank test, respectively.
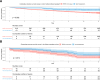
Results: The study included 61 ITA recipients matched to 610 T1D control patients and 45 IAK recipients matched to 45 T1D control patients over a median follow-up period >10 years. Compared with T1D control patients, ITA and IAK recipients had a lower composite outcome risk (HR 0.39 [95% CI 0.21-0.71; P = 0.002] and 0.52 [0.30-0.88; P = 0.014], respectively) that seemed driven by reduced mortality (0.22 [0.09-0.54]; P < 0.001) for ITA and reduced dialysis (0.19 [0.07-0.50]; P < 0.001) for IAK. Both groups showed no significant changes in cancer risk.
Conclusions: This study suggests long-term benefits of IT on diabetes-related outcomes. Furthermore, despite the use of immunosuppressive drugs following IT, we observed no significant increase in the risk of cancer. Altogether, these findings highlight a favorable risk-benefit ratio of IT in treating patients with unstable T1D.
© 2025 by the American Diabetes Association.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Pease A, Lo C, Earnest A, Kiriakova V, Liew D, Zoungas S.. The efficacy of technology in type 1 diabetes: a systematic review, network meta-analysis, and narrative synthesis. Diabetes Technol Ther 2020;22:411–421 - PubMed
-
- Brennan DC, Kopetskie HA, Sayre PH, et al. . Long-term follow-up of the Edmonton protocol of islet transplantation in the United States. Am J Transplant 2016;16:509–517 - PubMed
-
- Vantyghem M-C, Chetboun M, Gmyr V, et al. . Erratum. Ten-year outcome of islet alone or islet after kidney transplantation in type 1 diabetes: a prospective parallel-arm cohort study. Diabetes Care 2019;42:2042-2049. Diabetes Care 2020;43:1164–2049 - PubMed
-
- Lablanche S, Borot S, Wojtusciszyn A, et al. .; GRAGIL Network . Ten-year outcomes of islet transplantation in patients with type 1 diabetes: data from the Swiss-French GRAGIL Network. Am J Transplant 2021;21:3725–3733 - PubMed

