Dysfunctional cardiomyocyte signalling and heart disease
- PMID: 40245468
- PMCID: PMC7617817
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ceb.2025.102517
Dysfunctional cardiomyocyte signalling and heart disease
Abstract
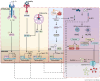
Cardiomyocyte signalling pathways are central to maintaining the structural and functional integrity of the heart. Dysregulation of these pathways contributes to the onset and progression of heart diseases, including heart failure, arrhythmias and cardiomyopathies. This review focuses on very recent work on dysfunctional cardiomyocyte signalling and its role in the pathophysiology of heart disease. We discuss key pathways, including immune signalling within cardiomyocytes, signalling associated with microtubule dysfunction, Hippo-yes-associated protein signalling and adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase signalling, highlighting how aberrations in their regulation lead to impaired cardiomyocyte functions and pinpointing the potential therapeutic opportunities in these pathways. This review underscores the complexity of cardiomyocyte signalling networks and emphasises the need for further dissecting signalling pathways to prevent cardiomyocyte dysfunction.
Copyright © 2025 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests: X.L. is an inventor on the UK patent ‘Treatment of Inflammatory Diseases’ (application no. 2313514.8).
Figures
Similar articles
-
How lived experiences of illness trajectories, burdens of treatment, and social inequalities shape service user and caregiver participation in health and social care: a theory-informed qualitative evidence synthesis.Health Soc Care Deliv Res. 2025 Jun;13(24):1-120. doi: 10.3310/HGTQ8159. Health Soc Care Deliv Res. 2025. PMID: 40548558
-
Comprehensive single-cell chromatin and transcriptomic profiling of peripheral immune cells in nonsegmental vitiligo.Br J Dermatol. 2025 Jun 20;193(1):115-124. doi: 10.1093/bjd/ljaf041. Br J Dermatol. 2025. PMID: 39888372
-
Cardiomyocyte maturation and its reversal during cardiac regeneration.Dev Dyn. 2024 Jan;253(1):8-27. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.557. Epub 2022 Dec 21. Dev Dyn. 2024. PMID: 36502296 Review.
-
Dusp14-Mediated Dephosphorylation of MLKL Protects Against Cardiomyocyte Necroptosis in Hypothyroidism-Induced Heart Failure.Circulation. 2025 Jun 24;151(25):1797-1813. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.125.074353. Epub 2025 May 13. Circulation. 2025. PMID: 40357546
-
Social network interventions to support cardiac rehabilitation and secondary prevention in the management of people with heart disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Jun 28;6(6):CD013820. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013820.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 37378598 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bers DM. Calcium cycling and signaling in cardiac myocytes. Annu Rev Physiol. 2008;70:23–49. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

