HDAC9-Mediated Pyroptosis Promotes Orthodontically Induced Inflammatory Root Resorption
- PMID: 40245750
- PMCID: PMC12142796
- DOI: 10.1016/j.identj.2025.03.018
HDAC9-Mediated Pyroptosis Promotes Orthodontically Induced Inflammatory Root Resorption
Abstract
Introduction and aims: Orthodontically induced inflammatory root resorption (OIIRR) is a common iatrogenic outcome of orthodontic treatment. Both epigenetic modifications and pyroptosis have demonstrated a certain role in OIIRR. This study aims to investigate whether epigenetic modifications regulate pyroptosis to be involved in OIIRR.
Method: Rat model of OIIRR was established, and the periodontal tissues were utilized for H&E staining, TRAP staining, immunofluorescence, transcriptome sequencing, and RT-qPCR analysis. Human periodontal ligament fibroblasts (hPDLFs) were overexpressed with HDAC9, treated with pyroptosis inhibitor, incubated with osteoclast, and then subjected to CUT&Tag sequencing.
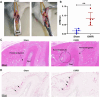
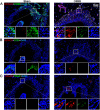
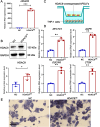
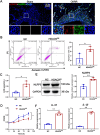
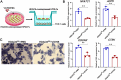
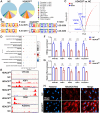
Results: Orthodontic force increased the distance of orthodontic tooth movement and the abundance of osteoclast. Transcriptome sequencing identified that Hdac9 was upregulated in the periodontal tissues of OIIRR rats compared to the control. Immunofluorescence revealed that HDAC9 was present in periodontal ligament fibroblasts, with reduced fluorescence of HDAC9 in OIIRR compared to the control. HDAC9 overexpression in hPDLFs induced pyroptosis and promoted osteoclast differentiation. These effects were reversed by pyroptosis inhibitor. CUT&Tag analysis showed that HDAC9 overexpression resulted in an enrichment of deacetylated genes on mitochondrial dysfunction-associated pathways. CUT&Tag-PCR analysis confirmed reduced H3K9ac enrichment on the mitochondrial dysfunction-associated genes VPS13D, AQP1, PEX2, CDK1, and PLEKHA1 after HDAC9 overexpression, and RT-qPCR analysis revealed a corresponding decrease in their respective expression levels. Accordingly, the ROS level was also increased by HDAC9 overexpression.
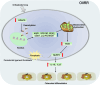
Conclusion: HDAC9-mediated histone deacetylation induces mitochondrial dysfunction and pyroptosis in hPDLFs, thereby promoting osteoclast differentiation and OIIRR progression.
Clinical relevance: This study reveals the regulatory mechanism of pyroptosis in OIIRR from the perspective of epigenetic modifications, providing new insights into the pathogenesis of OIIRR.
Keywords: HDAC9; Mitochondrial dysfunction; Orthodontically induced inflammatory root resorption; Periodontal ligament fibroblasts; Pyroptosis.
Copyright © 2025 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest None disclosed.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Effect of low-intensity pulsed ultrasound on the mineralization of force-treated cementoblasts and orthodontically induced inflammatory root resorption via the Lamin A/C-Yes associated protein axis.J Periodontal Res. 2025 Feb;60(2):189-199. doi: 10.1111/jre.13330. Epub 2024 Aug 2. J Periodontal Res. 2025. PMID: 39095980
-
Runx1/miR-26a/Jagged1 signaling axis controls osteoclastogenesis and alleviates orthodontically induced inflammatory root resorption.Int Immunopharmacol. 2021 Nov;100:107991. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2021.107991. Epub 2021 Aug 23. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34438336
-
LncRNA XIST regulates osteoclast formation and promotes orthodontically induced inflammatory root resorption through miR-130b-3p/PTEN axis.Biotechnol Genet Eng Rev. 2024 Nov;40(3):2560-2576. doi: 10.1080/02648725.2023.2200331. Epub 2023 Apr 14. Biotechnol Genet Eng Rev. 2024. PMID: 37057740
-
PD-L1, a Potential Immunomodulator Linking Immunology and Orthodontically Induced Inflammatory Root Resorption (OIIRR): Friend or Foe?Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Sep 27;23(19):11405. doi: 10.3390/ijms231911405. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36232704 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Potential Regulatory Role of Ferroptosis in Orthodontically Induced Inflammatory Root Resorption.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Dec 19;25(24):13617. doi: 10.3390/ijms252413617. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39769377 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

