Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Ensifentrine: A Novel, Selective Dual Inhibitor of Phosphodiesterase 3 and Phosphodiesterase 4
- PMID: 40245851
- PMCID: PMC12101800
- DOI: 10.1159/000545645
Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Ensifentrine: A Novel, Selective Dual Inhibitor of Phosphodiesterase 3 and Phosphodiesterase 4
Abstract
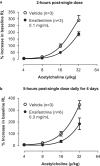
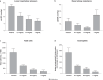
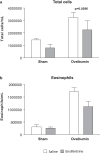
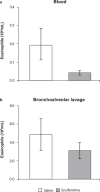
Ensifentrine is a novel, low-molecular-weight molecule that is a selective, dual inhibitor of phosphodiesterase (PDE)3 and PDE4. Inhibition of PDE3 has been shown to relax airway smooth muscle and inhibition of PDE4 to inhibit inflammatory responses and to stimulate the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator in human airway epithelial cells through accumulation of intracellular cyclic adenosine monophosphate. Additionally, the dual inhibition of PDE3 and PDE4 demonstrates enhanced or synergistic effects compared with inhibition of either PDE3 or PDE4 alone on contraction of airway smooth muscle and suppression of inflammatory responses. Ensifentrine inhalation suspension 3 mg was recently approved in the USA for the maintenance treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in adult patients and is marketed under the trade name Ohtuvayre™. This manuscript describes further evidence that ensifentrine is a selective dual inhibitor of both human PDE3 and PDE4 enzymes and that this drug has significant anti-inflammatory activity in vivo in both allergic guinea pigs and non-human primates. This dual bronchodilator and anti-inflammatory activity of ensifentrine makes it a promising strategy as a novel inhaled "bifunctional" drug for the treatment of obstructive and inflammatory diseases of the respiratory tract.
Keywords: Anti-inflammatory drugs; Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; Ensifentrine; PDE3 and PDE4; Phosphodiesterase inhibitors; RPL554.
© 2025 The Author(s). Published by S. Karger AG, Basel.
Conflict of interest statement
M.M.B. and T.R. are current employees of Verona Pharma. L.F. is a former employee of Verona Pharma. D.S., R.V., and D.A.S. are former paid consultants for Verona Pharma.
Figures
Similar articles
-
What role will ensifentrine play in the future treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease patients? Implications from recent clinical trials.Immunotherapy. 2023 Dec;15(18):1511-1519. doi: 10.2217/imt-2023-0136. Epub 2023 Oct 2. Immunotherapy. 2023. PMID: 37779474 Review.
-
The Phosphodiesterase Inhibitor Ensifentrine Reduces Production of Proinflammatory Mediators in Well Differentiated Bronchial Epithelial Cells by Inhibiting PDE4.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2020 Dec;375(3):414-429. doi: 10.1124/jpet.120.000080. Epub 2020 Oct 4. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2020. PMID: 33012706
-
Ensifentrine (RPL554): an investigational PDE3/4 inhibitor for the treatment of COPD.Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2019 Oct;28(10):827-833. doi: 10.1080/13543784.2019.1661990. Epub 2019 Sep 1. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2019. PMID: 31474120 Review.
-
Ensifentrine (RPL554): an inhaled 'bifunctional' dual PDE3/4 inhibitor for the treatment of asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.Pharm Pat Anal. 2018 Nov;7(6):249-257. doi: 10.4155/ppa-2018-0030. Epub 2019 Jan 18. Pharm Pat Anal. 2018. PMID: 30657422
-
Phosphodiesterase Inhibition as a Therapeutic Strategy for Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: Where We Have Been and What Lies Ahead.Chronic Obstr Pulm Dis. 2025 Jan 29;12(1):82-92. doi: 10.15326/jcopdf.2024.0559. Chronic Obstr Pulm Dis. 2025. PMID: 39688360 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Ensifentrine Plus a Long-Acting Muscarinic Antagonist in COPD: A Trifunctional Dual Bronchodilation Perspective.Drugs. 2025 Jul 24. doi: 10.1007/s40265-025-02213-w. Online ahead of print. Drugs. 2025. PMID: 40702257 Review.
References
-
- Abbott-Banner KH, Page CP. Dual PDE3/4 and PDE4 inhibitors: novel treatments for COPD and other inflammatory airway diseases. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2014;114(5):365–76. - PubMed
-
- Boswell-Smith V, Spina D, Oxford AW, Comer MB, Seeds EA, Page CP. The pharmacology of two novel long-acting phosphodiesterase 3/4 inhibitors, 10-dimethoxy-4H-pyrimido[6,1-a]isoquinolin-4-one]. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2006;318(2):840–8. - PubMed
-
- Franciosi LG, Diamant Z, Banner KH, Zuiker R, Morelli N, Kamerling IMC, et al. . Efficacy and safety of RPL554, a dual PDE3 and PDE4 inhibitor, in healthy volunteers and in patients with asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: findings from four clinical trials. Lancet Respir Med. 2013;1(9):714–27. - PubMed
-
- Rheault T, MacDonald-Berko M. Antiinflammatory pharmacology of ensifentrine. Chest. 2020;158(4):A2284.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

