Joule Heating-Driven sp2-C Domains Modulation in Biomass Carbon for High-Performance Bifunctional Oxygen Electrocatalysis
- PMID: 40246802
- PMCID: PMC12006640
- DOI: 10.1007/s40820-025-01725-0
Joule Heating-Driven sp2-C Domains Modulation in Biomass Carbon for High-Performance Bifunctional Oxygen Electrocatalysis
Abstract
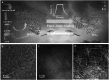
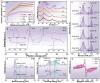
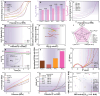
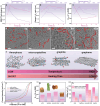
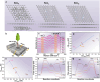
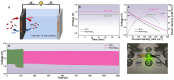
Natural biomass-derived carbon material is one promising alternative to traditional graphene-based catalyst for oxygen electrocatalysis. However, their electrocatalytic performance were constrained by the limited modulating strategy. Herein, using N-doped commercial coconut shell-derived activated carbon (AC) as catalyst model, the controllably enhanced sp2-C domains, through an flash Joule heating process, effectively improve the edge defect density and overall graphitization degree of AC catalyst, which tunes the electronic structure of N configurations and accelerates electron transfer, leading to excellent oxygen reduction reaction performance (half-wave potential of 0.884 VRHE, equivalent to commercial 20% Pt/C, with a higher kinetic current density of 5.88 mA cm-2) and oxygen evolution reaction activity (overpotential of 295 mV at 10 mA cm2). In a Zn-air battery, the catalyst shows outstanding cycle stability (over 1200 h) and a peak power density of 121 mW cm-2, surpassing commercial Pt/C and RuO2 catalysts. Density functional theory simulation reveals that the enhanced catalytic activity arises from the axial regulation of local sp2-C domains. This work establishes a robust strategy for sp2-C domain modulation, offering broad applicability in natural biomass-based carbon catalysts for electrocatalysis.
Keywords: sp 2-C domains; Carbon-based catalyst; Joule heating; Natural biomass; Oxygen electrocatalysis.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Conflict of Interest: The authors declare no interest conflict. They have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Q. Ni, S. Zhang, K. Wang, H. Guo, J. Zhang et al., Carbon quantum dot-mediated binary metal–organic framework nanosheets for efficient oxygen evolution at ampere-level current densities in proton exchange membrane electrolyzers. J. Mater. Chem. A 12(45), 31253–31261 (2024). 10.1039/D4TA06855F - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
