Hypoxia-induced Wnt5a-secreting fibroblasts promote colon cancer progression
- PMID: 40246836
- PMCID: PMC12006413
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-58748-9
Hypoxia-induced Wnt5a-secreting fibroblasts promote colon cancer progression
Abstract
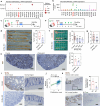
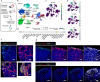
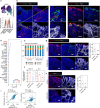
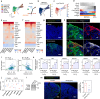
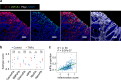
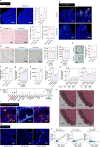
Wnt5a, a representative Wnt ligand that activates the β-catenin-independent pathway, has been shown to promote tumorigenesis. However, it is unclear where Wnt5a is produced and how it affects colon cancer aggressiveness. In this study, we demonstrate that Wnt5a is expressed in fibroblasts near the luminal side of the tumor, and its depletion suppresses mouse colon cancer formation. To characterize the specific fibroblast subtype, a meta-analysis of human and mouse colon fibroblast single-cell RNA-seq data is performed. The results show that Wnt5a is expressed in hypoxia-induced inflammatory fibroblast (InfFib), accompanied by the activation of HIF2. Moreover, Wnt5a maintains InfFib through the suppression of angiogenesis mediated by soluble VEGF receptor1 (Flt1) secretion from endothelial cells, thereby inducing further hypoxia. InfFib also produces epiregulin, which promotes colon cancer growth. Here, we show that Wnt5a acts on endothelial cells, inducing a hypoxic environment that maintains InfFib, thereby contributing to colon cancer progression through InfFib.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Brugger, M. D. & Basler, K. The diverse nature of intestinal fibroblasts in development, homeostasis, and disease. Trends Cell Biol33, 834–849 (2023). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 22K20791/MEXT | Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS)
- 23K14566/MEXT | Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS)
- 21K19407/MEXT | Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS)
- 23K18241/MEXT | Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS)
- 22K06932/MEXT | Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

