A comprehensive case study of deep learning on the detection of alpha thalassemia and beta thalassemia using public and private datasets
- PMID: 40246871
- PMCID: PMC12006322
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-97353-0
A comprehensive case study of deep learning on the detection of alpha thalassemia and beta thalassemia using public and private datasets
Abstract
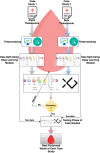
This study explores the performance of deep learning models, specifically Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) and XGBoost, in predicting alpha and beta thalassemia using both public and private datasets. Thalassemia is a genetic disorder that impairs hemoglobin production, leading to anemia and other health complications. Early diagnosis is essential for effective management and prevention of severe health issues. The study applied CNN and XGBoost to two case studies: one for alpha-thalassemia and the other for beta-thalassemia. Public datasets were sourced from medical databases, while private datasets were collected from clinical records, offering a more comprehensive feature set and larger sample sizes. After data preprocessing and splitting, model performance was evaluated. XGBoost achieved 99.34% accuracy on the private dataset for alpha thalassemia, while CNN reached 98.10% accuracy on the private dataset for beta-thalassemia. The superior performance on private datasets was attributed to better data quality and volume. This study highlights the effectiveness of deep learning in medical diagnostics, demonstrating that high-quality data can significantly enhance the predictive capabilities of AI models. By integrating CNN and XGBoost, this approach offers a robust method for detecting thalassemia, potentially improving early diagnosis and reducing disease-related mortality.
Keywords: Alpha thalassemia; Beta thalassemia; CNN; Case study; Deep learning; Thalassemia; XGBoost.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Conflicts of Interest: The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. Ethics approval and consent to participate: This study was approved by the Ethics committee of Riphah International University, Pakistan. Informed consent was obtained from all subjects. All the experimental procedures were performed by the standards of the Declaration of Helsinki 1964.
Figures

References
-
- Hirimutugoda, Y. M. & Wijayarathna, G. Image analysis system for detection of red cell disorders using artifcial neural networks. Sri Lanka J. Bio-Medical Inf.1 (1), 35 (2010).
-
- Zhuang, Q. et al. Te value of combined detection of HbA2 and HbF for the screening of thalassemia among individuals of childbearing ages. Zhonghua Yi Xue Yi Chuan Xue Za Zhi. 39 (1), 16–20 (2022). - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

