Cryo-EM structures of the small-conductance Ca2+-activated KCa2.2 channel
- PMID: 40246884
- PMCID: PMC12006403
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-59061-1
Cryo-EM structures of the small-conductance Ca2+-activated KCa2.2 channel
Abstract
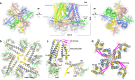
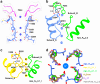
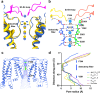
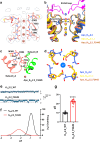
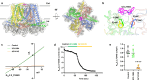
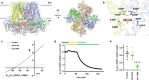
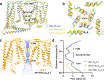
Small-conductance Ca2+-activated K+ (KCa2.1-KCa2.3) channels modulate neuronal and cardiac excitability. We report cryo-electron microscopy structures of the KCa2.2 channel in complex with calmodulin and Ca2+, alone or bound to two small molecule inhibitors, at 3.18, 3.50, 2.99 and 2.97 angstrom resolution, respectively. Extracellular S3-S4 loops in β-hairpin configuration form an outer canopy over the pore with an aromatic box at the canopy's center. Each S3-S4 β-hairpin is tethered to the selectivity filter in the neighboring subunit by inter-subunit hydrogen bonds. This hydrogen bond network flips the aromatic residue (Tyr362) in the filter's GYG signature by 180°, causing the outer selectivity filter to widen and water to enter the filter. Disruption of the tether by a mutation narrows the outer selectivity filter, realigns Tyr362 to the position seen in other K+ channels, and significantly increases unitary conductance. UCL1684, a mimetic of the bee venom peptide apamin, sits atop the canopy and occludes the opening in the aromatic box. AP14145, an analogue of a therapeutic for atrial fibrillation, binds in the central cavity below the selectivity filter and induces closure of the inner gate. These structures provide a basis for understanding the small unitary conductance and pharmacology of KCa2.x channels.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Kohler, M. et al. Small-conductance, calcium-activated potassium channels from mammalian brain. Science273, 1709–1714 (1996). - PubMed
-
- Xia, X. M. et al. Mechanism of calcium gating in small-conductance calcium-activated potassium channels. Nature395, 503–507 (1998). - PubMed
-
- Adelman, J. P., Maylie, J. & Sah, P. Small-conductance Ca2+-activated K+ channels: form and function. Annu. Rev. Physiol.74, 245–269 (2012). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R15 NS130420/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS131467/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- U24 GM129541/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL059949/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 4R33NS101182-03/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

