Imaging 3D cell cultures with optical microscopy
- PMID: 40247123
- PMCID: PMC12402705
- DOI: 10.1038/s41592-025-02647-w
Imaging 3D cell cultures with optical microscopy
Abstract
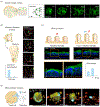
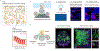
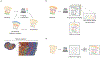
Three-dimensional (3D) cell cultures have gained popularity in recent years due to their ability to represent complex tissues or organs more faithfully than conventional two-dimensional (2D) cell culture. This article reviews the application of both 2D and 3D microscopy approaches for monitoring and studying 3D cell cultures. We first summarize the most popular optical microscopy methods that have been used with 3D cell cultures. We then discuss the general advantages and disadvantages of various microscopy techniques for several broad categories of investigation involving 3D cell cultures. Finally, we provide perspectives on key areas of technical need in which there are clear opportunities for innovation. Our goal is to guide microscope engineers and biomedical end users toward optimal imaging methods for specific investigational scenarios and to identify use cases in which additional innovations in high-resolution imaging could be helpful.
© 2025. Springer Nature America, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: J.T.C.L. is a cofounder, equity holder and board member of Alpenglow Biosciences. A.K.G. is a cofounder and equity holder of Alpenglow Biosciences. N.L.A. and Y.W. are cofounders and equity holders of Altis Biosystems. B.S.F. is an inventor on patents and patent applications related to human organoid differentiation and disease modeling (US20200377860A1, WO2019222559A1). B.S.F. holds ownership interest in Plurexa. The remaining authors report no conflicts of interest.
Figures

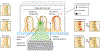


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R01DK120606/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- U54DK137328/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- W81XWH-20-1-0851/U.S. Department of Defense (United States Department of Defense)
- R01CA268207/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- R00 CA240681/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R00CA240681/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- U01 AI176460/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U2CTR004867/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- R01 EB031002/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- U01AI176460/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- U01 DK127553/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R41 DK136452/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA268207/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK120606/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UC2 DK126006/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01DK127553/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- R01 DK138948/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01DK138948/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- U54 DK137328/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U2C TR004867/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UC2DK126006/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | National Institutes of Health (NIH)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

